Sid2p, a spindle pole body kinase that regulates the onset of cytokinesis
- PMID: 10459013
- PMCID: PMC2156147
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.146.4.777
Sid2p, a spindle pole body kinase that regulates the onset of cytokinesis
Abstract
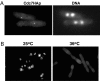
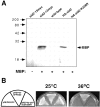
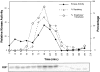
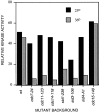
The fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe divides by medial fission through the use of an actomyosin contractile ring. Precisely at the end of anaphase, the ring begins to constrict and the septum forms. Proper coordination of cell division with mitosis is crucial to ensure proper segregation of chromosomes to daughter cells. The Sid2p kinase is one of several proteins that function as part of a novel signaling pathway required for initiation of medial ring constriction and septation. Here, we show that Sid2p is a component of the spindle pole body at all stages of the cell cycle and localizes transiently to the cell division site during medial ring constriction and septation. A medial ring and an intact microtubule cytoskeleton are required for the localization of Sid2p to the division site. We have established an in vitro assay for measuring Sid2p kinase activity, and found that Sid2p kinase activity peaks during medial ring constriction and septation. Both Sid2p localization to the division site and activity depend on the function of all of the other septation initiation genes: cdc7, cdc11, cdc14, sid1, spg1, and sid4. Thus, Sid2p, a component of the spindle pole body, by virtue of its transient localization to the division site, appears to determine the timing of ring constriction and septum delivery in response to activating signals from other Sid gene products.
Figures
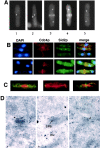
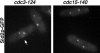
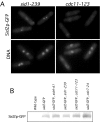
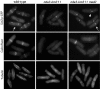
Similar articles
-
Mob1p interacts with the Sid2p kinase and is required for cytokinesis in fission yeast.Curr Biol. 2000 May 18;10(10):619-22. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00492-9. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10837231
-
Cytokinetic actomyosin ring formation and septation in fission yeast are dependent on the full recruitment of the polo-like kinase Plo1 to the spindle pole body and a functional spindle assembly checkpoint.J Cell Sci. 2002 Sep 15;115(Pt 18):3575-86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00031. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12186944
-
The role of the sid1p kinase and cdc14p in regulating the onset of cytokinesis in fission yeast.EMBO J. 2000 Apr 17;19(8):1803-15. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.8.1803. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10775265 Free PMC article.
-
Studies in fission yeast on mechanisms of cell division site placement.Cell Struct Funct. 2001 Dec;26(6):539-44. doi: 10.1247/csf.26.539. Cell Struct Funct. 2001. PMID: 11942607 Review.
-
Microtubule and actin-dependent movement of the formin cdc12p in fission yeast.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Apr 15;49(2):161-7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(20000415)49:2<161::AID-JEMT8>3.0.CO;2-2. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10816255 Review.
Cited by
-
Ensuring the faithful execution of cytokinesis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Commun Integr Biol. 2012 May 1;5(3):265-71. doi: 10.4161/cib.19860. Commun Integr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22896789 Free PMC article.
-
The role of anillin/Mid1p during medial division and cytokinesis: from fission yeast to cancer cells.Cell Cycle. 2023 Mar-Mar;22(6):633-644. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2147655. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 36426865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correct regulation of the septation initiation network in Schizosaccharomyces pombe requires the activities of par1 and par2.Genetics. 2001 Aug;158(4):1413-29. doi: 10.1093/genetics/158.4.1413. Genetics. 2001. PMID: 11514436 Free PMC article.
-
Fission yeast cdc31p is a component of the half-bridge and controls SPB duplication.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jul;14(7):2793-808. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-10-0661. Epub 2003 Apr 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12857865 Free PMC article.
-
Sid4p is required to localize components of the septation initiation pathway to the spindle pole body in fission yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 May 9;97(10):5249-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5249. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10805785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bähler J., Wu J.Q., Longtine M.S., Shah N.G., McKenzie A.R., Steever A.B., Wach A., Philippsen P., Pringle J.R. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe Yeast 14 1998. 943 951b - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian M.K., Helfman D.M., Hemmingsen S.M. A new tropomyosin essential for cytokinesis in the fission yeast S. pombe . Nature. 1992;360:84–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

