Synaptic control of glycine and GABA(A) receptors and gephyrin expression in cultured motoneurons
- PMID: 10460250
- PMCID: PMC6782513
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-17-07434.1999
Synaptic control of glycine and GABA(A) receptors and gephyrin expression in cultured motoneurons
Abstract
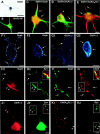
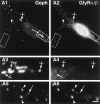
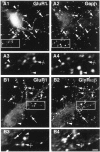
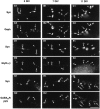
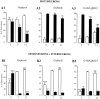
We have evaluated the influence of the secretory phenotype of presynaptic boutons on the accumulation of postsynaptic glycine receptors (GlyRs), type A GABA receptors (GABA(A)Rs), and gephyrin clusters. The cellular distribution of these components was analyzed on motoneurons cultured either alone or with glycinergic and/or GABAergic neurons. In motoneurons cultured alone, we observed gephyrin clusters at nonsynaptic sites and in front of cholinergic boutons, whereas glycine and GABA(A) receptors formed nonsynaptic clusters. These receptors are functionally and pharmacologically similar to those found in cultures of all spinal neurons. Motoneurons receiving GABAergic innervation from dorsal root ganglia neurons displayed postsynaptic clusters of gephyrin and GABA(A)Rbeta but not of GlyRalpha/beta subunits. In motoneurons receiving glycinergic and GABAergic innervation from spinal interneurons, gephyrin, GlyRalpha/beta, and GABA(A)Rbeta formed mosaics at synaptic loci. These results indicate that (1) the transmitter phenotype of the presynaptic element determines the postsynaptic accumulation of specific receptors but not of gephyrin and (2) the postsynaptic accumulation of gephyrin alone cannot account for the formation of GlyR-rich microdomains.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Formation of mixed glycine and GABAergic synapses in cultured spinal cord neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Nov;12(11):3883-92. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00271.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11069583
-
Glycine and GABA(A) receptor subunits on Renshaw cells: relationship with presynaptic neurotransmitters and postsynaptic gephyrin clusters.J Comp Neurol. 2002 Mar 12;444(3):275-89. doi: 10.1002/cne.10148. J Comp Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11840480
-
Loss of postsynaptic GABA(A) receptor clustering in gephyrin-deficient mice.J Neurosci. 1999 Nov 1;19(21):9289-97. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-21-09289.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10531433 Free PMC article.
-
Gephyrin: a master regulator of neuronal function?Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014 Mar;15(3):141-56. doi: 10.1038/nrn3670. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24552784 Review.
-
Mini-review: gephyrin, a major postsynaptic protein of GABAergic synapses.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Jul;12(7):2205-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00106.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10947798 Review.
Cited by
-
Receptors, gephyrin and gephyrin-associated proteins: novel insights into the assembly of inhibitory postsynaptic membrane specializations.J Physiol. 2000 May 15;525 Pt 1(Pt 1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-4-00001.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10811719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycinergic neurotransmission in the rostral ventrolateral medulla controls the time course of baroreflex-mediated sympathoinhibition.J Physiol. 2019 Jan;597(1):283-301. doi: 10.1113/JP276467. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30312491 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial patterning of excitatory and inhibitory neuropil territories during spinal circuit development.J Comp Neurol. 2017 May 1;525(7):1649-1667. doi: 10.1002/cne.24152. J Comp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 27997694 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of alpha1, alpha4, gamma2, and delta subunits of GABAA receptors in hippocampal granule cells.Brain Res. 2004 Dec 17;1029(2):207-16. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.09.056. Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15542076 Free PMC article.
-
Pax6 and engrailed 1 regulate two distinct aspects of renshaw cell development.J Neurosci. 2004 Feb 4;24(5):1255-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3187-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14762144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez FJ, Dewey DE, Harrington DA, Fyffe REW. Cell-type specific organization of glycine receptor clusters in the mammalian spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1997;379:150–170. - PubMed
-
- Baude A, Sequier JM, McKernan RM, Olivier KR, Somogyi P. Differential subcellular distribution of the α6 subunit versus the α1 and β2/3 subunits of the GABAA benzodiazepine receptor complex in granule cells of the cerebellar cortex. Neuroscience. 1992;51:739–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
