Reduction of adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate instead of 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate in cysteine biosynthesis by Rhizobium meliloti and other members of the family Rhizobiaceae
- PMID: 10464198
- PMCID: PMC94033
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.17.5280-5287.1999
Reduction of adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate instead of 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate in cysteine biosynthesis by Rhizobium meliloti and other members of the family Rhizobiaceae
Abstract
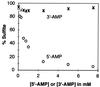
We have cloned and sequenced three genes from Rhizobium meliloti (Sinorhizobium meliloti) that are involved in sulfate activation for cysteine biosynthesis. Two of the genes display homology to the Escherichia coli cysDN genes, which code for an ATP sulfurylase (EC 2.7.7.4). The third gene has homology to the E. coli cysH gene, a 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) reductase (EC 1.8.99.4), but has greater homology to a set of genes found in Arabidopsis thaliana that encode an adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (APS) reductase. In order to determine the specificity of the R. meliloti reductase, the R. meliloti cysH homolog was histidine tagged and purified, and its specificity was assayed in vitro. Like the A. thaliana reductases, the histidine-tagged R. meliloti cysH gene product appears to favor APS over PAPS as a substrate, with a Km for APS of 3 to 4 microM but a Km for PAPS of >100 microM. In order to determine whether this preference for APS is unique to R. meliloti among members of the family Rhizobiaceae or is more widespread, cell extracts from R. leguminosarum, Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234, Rhizobium fredii (Sinorhizobium fredii), and Agrobacterium tumefaciens were assayed for APS or PAPS reductase activity. Cell extracts from all four species also preferentially reduce APS over PAPS.
Figures



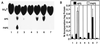


References
-
- Arz H E, Gisselmann G, Schiffmann S, Schwenn J D. A cDNA for adenylyl sulphate (APS)-kinase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1218:447–452. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: Greene Publishing Associates, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1994.
-
- Banfalvi Z, Kondorosi A. Production of root hair deformation factors by Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes in Escherichia coli: hsnD (nodH) is involved in the plant host-specific modification of the nodABC factor. Plant Mol Biol. 1989;13:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Carlson R W, Price N P J, Stacey G. The biosynthesis of rhizobial lipo-oligosaccharide nodulation signal molecules. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 1994;7:684–695. - PubMed
-
- Cedergren R A, Lee J, Ross K L, Hollingsworth R I. Common links in the structure and cellular localization of Rhizobium chitolipooligosaccharides and general Rhizobium membrane phospholipid and glycolipid components. Biochemistry. 1995;34:4467–4477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

