Kinetics of serum soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor (TNF-R) type-I and type-II after a single interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) injection in chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 10469062
- PMCID: PMC1905374
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00992.x
Kinetics of serum soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor (TNF-R) type-I and type-II after a single interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) injection in chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
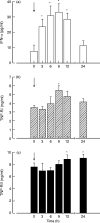
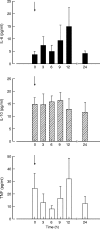
Circulating soluble TNF receptors, which act as TNF inhibitors, increase following the administration of IFN-alpha. Whether this is due to a direct IFN action or to indirect mechanisms involving the release of other cytokines is unclear. The kinetics of serum IFN, TNF, IL-6, IL-10, soluble TNF receptor type-I (sTNF-RI) and sTNF-RII were evaluated by enzyme immunoassays in 11 patients with chronic hepatitis C, following the first dose of recombinant human IFN-alpha2b (3 MU given subcutaneously). sTNF-RI concentrations paralleled IFN concentrations, rising from a mean +/- s.e.m. value of 3.5 +/- 0.3 ng/ml at baseline to a peak value of 5.5 +/- 0.5 ng/ml after 9 h, followed by a return to 4.1 +/- 0.4 ng/ml after 24 h (P = 0.0001). sTNF-RII concentrations, which were 7.6 +/- 0.5 ng/ml at baseline, fell initially to 6.9 +/- 0.5 ng/ml, to reach a peak at 24 h of 9.0 +/- 0.7 ng/ml (P < 0.0001). In contrast, the concentrations of TNF, IL-6 and IL-10 fluctuated with no significant changes at any time point. The area under the curve (AUC) of incremental IFN values had a strong positive correlation with the AUC of incremental sTNF-RI values (r = 0.75, P < 0.01). In patients with hepatitis C, IFN concentrations reached after a single dose of IFN were paralleled by correlationally increased concentrations of sTNF-RI, which are a much better marker of administered IFN than sTNF-RII, IL-6 or IL-10.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and soluble TNF receptors in patients with bulimia nervosa.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2000 Sep;53(3):383-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.2000.01091.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2000. PMID: 10971457
-
Increased serum leptin concentrations correlate with soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor levels in patients with cirrhosis.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2002 Dec;57(6):805-11. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.2002.01672.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2002. PMID: 12460331
-
Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in chronic hepatitis C: a correlation with histological fibrosis and activity.J Hepatol. 1999 Feb;30(2):185-91. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80060-9. J Hepatol. 1999. PMID: 10068094
-
PEGylated recombinant human soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor type I (r-Hu-sTNF-RI): novel high affinity TNF receptor designed for chronic inflammatory diseases.Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Nov;58 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):I73-81. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.2008.i73. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999. PMID: 10577978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of PEGylated soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor type I (PEG sTNF-RI) for chronic inflammatory diseases.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003 Sep 26;55(10):1315-36. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(03)00112-1. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003. PMID: 14499710 Review.
Cited by
-
Soluble inflammatory markers as predictors of liver histological changes in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010 Sep;29(9):1153-61. doi: 10.1007/s10096-010-0981-4. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20559676
-
Effect of alpha 2b interferon on inducement of mIL-2R and treatment of HCV in PBMC from patients with chronic viral hepatitis C.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Apr;9(4):751-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.751. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12679925 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 expression is upregulated in dendritic cells in patients with chronic HCV who respond to therapy.Hepat Res Treat. 2010;2010:429243. doi: 10.1155/2010/429243. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Hepat Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 21152182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davis GL, Balart LA, Schiff ER, et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with recombinant interferon alpha: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1501–5. - PubMed
-
- Di Bisceglie AM, Martin P, Kassianides C, et al. Recombinant interferon alpha therapy for chronic hepatitis C: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1506–10. - PubMed
-
- Peters M. Mechanism of action of interferons. Semin Liver Dis. 1989;9:235–9. - PubMed
-
- Stoffa R, Burgess SJ, Peters M. Clinical pharmacology of anti-viral agents. In: Zakim D, Boyer TD, editors. Hepatology A textbook of liver disease. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co; 1996. pp. 1293–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

