Use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses
- PMID: 10472982
- PMCID: PMC7055985
Use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses
Abstract
The differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses is frequently impossible with conventional MR imaging. We report two cases of cerebral abscesses that showed high signal on diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging and a strongly reduced apparent diffusion coefficient. This appearance was not present in our cases of necrotic/cystic gliomas (eight cases) and necrotic metastases (two cases). We believe that diffusion-weighted MR imaging may be a diagnostic clue in cases of cerebral "ring-enhancing" masses.
Figures

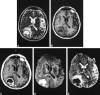
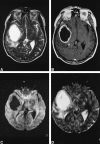

Comment in
-
Imaging brain abscesses with diffusion-weighted and other sequences.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999 Aug;20(7):1193-4. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999. PMID: 10472970 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging of cerebral abscess and subdural empyema.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000 Jun-Jul;21(6):1172. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. PMID: 10871036 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Osborn AG. Pyogenic Parenchymal Infections. In: Osborn AG, ed. Diagnostic Neuroradiology St. Louis, MO: Mosby Year-Book; 1994;688-692
-
- Ott D, Hennig J, Ernst T. Human brain tumors: assessment with in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 1993;186:745-752 - PubMed
-
- Schumacher DJ, Nelson TR, van Sonnenberg E, Meng TC, Hlavin P. Quantification of amino acids in human body fluids by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a specific test for the identification of abscess. Invest Radiol 1992;27:999-1004 - PubMed
-
- T Ebisu, C Tanaka, M Umeda, et al. Discrimination of brain abscess from necrotic or cystic tumors by diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 1996;14:1113-1116 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
