Identification of the Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1 toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase regulatory gene (touR) and of its cognate promoter
- PMID: 10473416
- PMCID: PMC99741
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.9.4057-4063.1999
Identification of the Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1 toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase regulatory gene (touR) and of its cognate promoter
Abstract
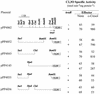
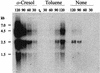
Toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase is an enzymatic complex, encoded by the touABCDEF genes, responsible for the early stages of toluene and o-xylene degradation in Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1. In order to identify the loci involved in the transcriptional regulation of the tou gene cluster, deletion analysis and complementation studies were carried out with Pseudomonas putida PaW340 as a heterologous host harboring pFB1112, a plasmid that allowed regulated expression, inducible by toluene and o-xylene and their corresponding phenols, of the toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase. A locus encoding a positive regulator, designated touR, was mapped downstream from the tou gene cluster. TouR was found to be similar to transcriptional activators of aromatic compound catabolic pathways belonging to the NtrC family and, in particular, to DmpR (83% similarity), which controls phenol catabolism. By using a touA-C2,3O fusion reporter system and by primer extension analysis, a TouR cognate promoter (P(ToMO)) was mapped, which showed the typical -24 TGGC, -12 TTGC sequences characteristic of sigma(54)-dependent promoters and putative upstream activating sequences. By using the reporter system described, we found that TouR responds to mono- and dimethylphenols, but not the corresponding methylbenzenes. In this respect, the regulation of the P. stutzeri system differs from that of other toluene or xylene catabolic systems, in which the hydrocarbons themselves function as effectors. Northern analyses indicated low transcription levels of tou structural genes in the absence of inducers. Basal toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase activity may thus transform these compounds to phenols, which then trigger the TouR-mediated response.
Figures

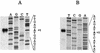
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

