Bactericidal activity of photocatalytic TiO(2) reaction: toward an understanding of its killing mechanism
- PMID: 10473421
- PMCID: PMC99746
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.9.4094-4098.1999
Bactericidal activity of photocatalytic TiO(2) reaction: toward an understanding of its killing mechanism
Abstract
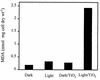
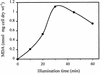
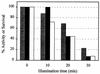
When titanium dioxide (TiO(2)) is irradiated with near-UV light, this semiconductor exhibits strong bactericidal activity. In this paper, we present the first evidence that the lipid peroxidation reaction is the underlying mechanism of death of Escherichia coli K-12 cells that are irradiated in the presence of the TiO(2) photocatalyst. Using production of malondialdehyde (MDA) as an index to assess cell membrane damage by lipid peroxidation, we observed that there was an exponential increase in the production of MDA, whose concentration reached 1.1 to 2.4 nmol. mg (dry weight) of cells(-1) after 30 min of illumination, and that the kinetics of this process paralleled cell death. Under these conditions, concomitant losses of 77 to 93% of the cell respiratory activity were also detected, as measured by both oxygen uptake and reduction of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride from succinate as the electron donor. The occurrence of lipid peroxidation and the simultaneous losses of both membrane-dependent respiratory activity and cell viability depended strictly on the presence of both light and TiO(2). We concluded that TiO(2) photocatalysis promoted peroxidation of the polyunsaturated phospholipid component of the lipid membrane initially and induced major disorder in the E. coli cell membrane. Subsequently, essential functions that rely on intact cell membrane architecture, such as respiratory activity, were lost, and cell death was inevitable.
Figures
References
-
- Akasaka S, Yamamoto K. Mutagenesis resulting from DNA damage by lipid peroxidation in the supF gene of Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1994;315:105–112. - PubMed
-
- Aust S. Lipid peroxidation. In: Greenwald R A, editor. CRC handbook of methods for oxygen radical research. Boca Raton, Fla: CRC Press, Inc.; 1987. pp. 203–207.
-
- Blake D M, Maness P-C, Huang Z, Wolfrum E J, Jacoby W A, Huang J. Application of the photocatalytic chemistry of titanium dioxide to disinfection and the killing of cancer cells. Sep Purif Methods. 1999;28:1–50.
-
- Burcham P C, Kuhan Y T. Introduction of carbonyl groups into proteins by the lipid peroxidation product, malondialdehyde. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;220:996–1001. - PubMed
-
- Byrne J A, Eggins B R, Brown N M D, McKinnery B, Rouse M. Immobilisation of TiO2 powder for the treatment of polluted water. Appl Catal B Environ. 1998;17:25–36.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

