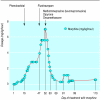
Morphine induced allodynia in a child with brain tumour
- PMID: 10473483
- PMCID: PMC1116494
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.319.7210.627
Morphine induced allodynia in a child with brain tumour
Figures
Comment in
-
Morphine induced allodynia in child with brain tumour. Signs are more likely to have been due to underlying medical condition.BMJ. 2000 Feb 5;320(7231):381. BMJ. 2000. PMID: 10657347 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Christrup LL. Morphine metabolites. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1997;41:116–122. - PubMed
-
- Glare PA, Walsh TD. Clinical pharmacokinetics of morphine. Ther Drug Monitoring. 1991;13:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Smith MT, Watt JA, Cramond T. Morphine-3-glucuronide—a potent antagonist of morphine analgesia. Life Sci. 1990;47:579–585. - PubMed
-
- Berde C, Ablin A, Glazer J, Miser A, Shapiro B, Weismann S, et al. American Academy of Pediatrics report of the Subcommittee on Disease-Related Pain in Childhood Cancer. Pediatrics. 1990;86:818–825. - PubMed
-
- Sjogren P, Jensen NH, Jensen TS. Disappearance of morphine-induced hyperalgesia after discontinuing or substituting morphine with other opioid agonists. Pain. 1994;59:313–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical