A reverse-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for verocytotoxin 1 and 2 antibodies in human and bovine sera
- PMID: 10473521
- PMCID: PMC95758
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.6.5.701-704.1999
A reverse-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for verocytotoxin 1 and 2 antibodies in human and bovine sera
Abstract
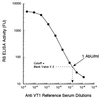
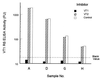
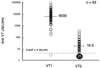
A reverse-sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), in which an antibody is sandwiched by antigens, was established for the titration of antibodies to verocytotoxins (VT) in human and animal sera. This assay has two advantages over a conventional indirect ELISA: (i) higher specificity and sensitivity and (ii) the ability to comparably titrate antibodies from different species. The VT1 (Shiga-like toxin 1) antibody-positive rates were 5% in 202 normal adult humans and 99% in 93 normal cattle at a dairy farm. This ELISA is most suitable for seroepidemiologic studies of infections with VT-producing Escherichia coli in humans and various animal species.
Figures
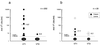


Similar articles
-
Comparison of the western blot assay with the neutralizing-antibody and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for measuring antibody to verocytotoxin 1.J Clin Microbiol. 1997 Mar;35(3):609-13. doi: 10.1128/jcm.35.3.609-613.1997. J Clin Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9041398 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization receptor-based immunoassay for detection of neutralizing antibodies to Escherichia coli verocytotoxin 1.J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2830-3. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2830-2833.1990. J Clin Microbiol. 1990. PMID: 2280020 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies to Escherichia coli Vero cytotoxin 1.J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jun;32(6):1457-63. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.6.1457-1463.1994. J Clin Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 8077389 Free PMC article.
-
The nature of immunity to the Escherichia coli Shiga toxins (verocytotoxins) and options for toxoid immunization.Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1998;51 Suppl:S26-35. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.51.supplement1_s26. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1998. PMID: 10211434 Review. No abstract available.
-
Shiga/verocytotoxins and Shiga/verotoxigenic Escherichia coli in animals.Vet Res. 1999 Mar-Jun;30(2-3):235-57. Vet Res. 1999. PMID: 10367357 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Response in Calves Vaccinated with Type Three Secretion System Antigens and Shiga Toxin 2B Subunit of Escherichia coli O157:H7.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 3;12(1):e0169422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169422. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28046078 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse ELISA for the detection of anti West Nile virus IgG antibodies in humans.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007 Jul;26(7):467-73. doi: 10.1007/s10096-007-0309-1. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17554572
-
Performance Evaluation of a Prototype Architect Antibody Assay for Babesia microti.J Clin Microbiol. 2018 Jul 26;56(8):e00460-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00460-18. Print 2018 Aug. J Clin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29743308 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative ELISA for monitoring the secretion of ZZ-fusion proteins using SpA domain as immunodetection reporter system.Mol Biotechnol. 2001 Nov;19(3):239-44. doi: 10.1385/MB:19:3:239. Mol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11721620
-
Development and application of a double-antigen sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to porcine circovirus 2.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012 Sep;19(9):1480-6. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00234-12. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22815145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrett T J, Green J H, Griffin P M, Pavia A T, Ostroff S M, Wachsmuth I K. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detecting antibodies to Shiga-like toxin I, Shiga-like toxin II and Escherichia coli in human serum. Curr Microbiol. 1991;23:189–195.
-
- Caprioli A, Luzzi I, Rosmini F, Pasquini P, Cirrincione R, Gianviti A, Matteucci M C, Rizzoni G. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome and Vero cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli infection in Italy. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:154–158. - PubMed
-
- Ito H, Yutsudo T, Hirayama T, Takeda Y. Isolation and some properties of A and B subunits of Vero toxin 2 and in vitro formation of hybrid toxins between subunits of Vero toxin 1 and Vero toxin 2 from Escherichia coli O157:H7. Microb Pathog. 1988;5:189–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

