Detection of antibodies to Brucella cytoplasmic proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurobrucellosis
- PMID: 10473531
- PMCID: PMC95768
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.6.5.756-759.1999
Detection of antibodies to Brucella cytoplasmic proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurobrucellosis
Abstract
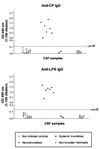
The diagnosis of human neurobrucellosis usually relies on the detection of antibodies to Brucella lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by agglutination tests or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Here we describe the detection of immunoglobulin G (IgG) to cytoplasmic proteins (CP) of Brucella spp. by ELISA and Western blotting in seven CSF samples from five patients with neurobrucellosis. While IgG to CP (titers of 200 to 12, 800) and IgG to LPS (800 to 6,400) were found in the CSF of these patients, these antibodies were not detected in CSF samples from two patients who had systemic brucellosis without neurological involvement. The latter, however, had serum IgG and IgM to both LPS and CP. No reactivity to these antigens was found in CSF samples from 14 and 20 patients suffering from nonbrucellar meningitis and noninfectious diseases, respectively. These findings suggest that, in addition to its usefulness in the serological diagnosis of human systemic brucellosis, the ELISA with CP antigen can be used for the specific diagnosis of human neurobrucellosis.
Figures

References
-
- Araj G F, Lulu A R, Saadah M A, Mousa A M, Strannegard I L, Shakir R A. Rapid diagnosis of central nervous system brucellosis by ELISA. J Neuroimmunol. 1986;12:173–182. - PubMed
-
- Araj G F, Lulu A R, Khateeb M I, Saadah M A, Shakir R A. ELISA versus routine tests in the diagnosis of patients with systemic and neurobrucellosis. APMIS. 1988;96:171–176. - PubMed
-
- Baldi P C, Wanke M M, Loza M E, Fossati C A. Brucella abortus cytoplasmic proteins used as antigens in an ELISA potentially useful for the diagnosis of canine brucellosis. Vet Microbiol. 1994;41:127–134. - PubMed
-
- Baldi P C, Giambartolomei G H, Goldbaum F A, Abdón L F, Velikovsky C A, Kittelberger R, Fossati C A. Humoral immune response against lipopoly saccharide and cytoplasmic proteins of Brucella abortus in cattle vaccinated with B. abortus S19 or experimentally infected with Yersinia enterocolitica serotype 0:9. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1996;3:472–476. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

