Division of labor among the alpha6beta4 integrin, beta1 integrins, and an E3 laminin receptor to signal morphogenesis and beta-casein expression in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 10473629
- PMCID: PMC25520
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.9.2817
Division of labor among the alpha6beta4 integrin, beta1 integrins, and an E3 laminin receptor to signal morphogenesis and beta-casein expression in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
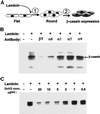
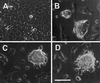
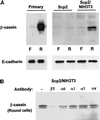
Contact of cultured mammary epithelial cells with the basement membrane protein laminin induces multiple responses, including cell shape changes, growth arrest, and, in the presence of prolactin, transcription of the milk protein beta-casein. We sought to identify the specific laminin receptor(s) mediating the multiple cell responses to laminin. Using assays with clonal mammary epithelial cells, we reveal distinct functions for the alpha6beta4 integrin, beta1 integrins, and an E3 laminin receptor. Signals from laminin for beta-casein expression were inhibited in the presence of function-blocking antibodies against both the alpha6 and beta1 integrin subunits and by the laminin E3 fragment. The alpha6-blocking antibody perturbed signals mediated by the alpha6beta4 integrin, and the beta1-blocking antibody perturbed signals mediated by another integrin, the alpha subunit(s) of which remains to be determined. Neither alpha6- nor beta1-blocking antibodies perturbed the cell shape changes resulting from cell exposure to laminin. However, the E3 laminin fragment and heparin both inhibited cell shape changes induced by laminin, thereby implicating an E3 laminin receptor in this function. These results elucidate the multiplicity of cell-extracellular matrix interactions required to integrate cell structure and signaling and ultimately permit normal cell function.
Figures