A p90(rsk) mutant constitutively interacting with MAP kinase uncouples MAP kinase from p34(cdc2)/cyclin B activation in Xenopus oocytes
- PMID: 10473640
- PMCID: PMC25542
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.9.2971
A p90(rsk) mutant constitutively interacting with MAP kinase uncouples MAP kinase from p34(cdc2)/cyclin B activation in Xenopus oocytes
Abstract
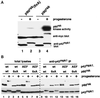
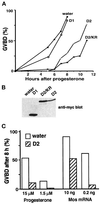
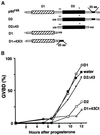
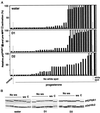
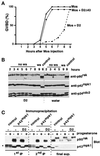
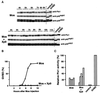
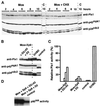
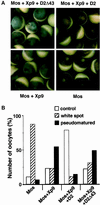
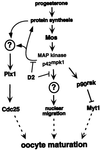
The efficient activation of p90(rsk) by MAP kinase requires their interaction through a docking site located at the C-terminal end of p90(rsk). The MAP kinase p42(mpk1) can associate with p90(rsk) in G(2)-arrested but not in mature Xenopus oocytes. In contrast, an N-terminally truncated p90(rsk) mutant named D2 constitutively interacts with p42(mpk1). In this report we show that expression of D2 inhibits Xenopus oocyte maturation. The inhibition requires the p42(mpk1) docking site. D2 expression uncouples the activation of p42(mpk1) and p34(cdc2)/cyclin B in response to progesterone but does not prevent signaling through p90(rsk). Instead, D2 interferes with a p42(mpk1)-triggered pathway, which regulates the phosphorylation and activation of Plx1, a potential activator of the Cdc25 phosphatase. This new pathway that links the activation of p42(mpk1) and Plx1 during oocyte maturation is independent of p34(cdc2)/cyclin B activity but requires protein synthesis. Using D2, we also provide evidence that the sustained activation of p42(mpk1) can trigger nuclear migration in oocytes. Our results indicate that D2 is a useful tool to study MAP kinase function(s) during oocyte maturation. Truncated substrates such as D2, which constitutively interact with MAP kinases, may also be helpful to study signal transduction by MAP kinases in other cellular processes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A link between MAP kinase and p34(cdc2)/cyclin B during oocyte maturation: p90(rsk) phosphorylates and inactivates the p34(cdc2) inhibitory kinase Myt1.EMBO J. 1998 Sep 1;17(17):5037-47. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.17.5037. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9724639 Free PMC article.
-
The critical role of the MAP kinase pathway in meiosis II in Xenopus oocytes is mediated by p90(Rsk).Curr Biol. 2000 Apr 20;10(8):430-8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00425-5. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10801413
-
A MAP kinase docking site is required for phosphorylation and activation of p90(rsk)/MAPKAP kinase-1.Curr Biol. 1999 Mar 11;9(5):281-4. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80120-1. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10074458
-
The activation of MAP kinase and p34cdc2/cyclin B during the meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2000;4:131-43. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4253-7_12. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2000. PMID: 10740821 Review.
-
Regulation of the meiotic cell cycle in oocytes.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;12(6):666-75. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00150-2. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11063930 Review.
Cited by
-
Ribosomal S6 Kinase Regulates the Timing and Entrainment of the Mammalian Circadian Clock Located in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus.Neuroscience. 2023 Apr 15;516:15-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2023.02.003. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Neuroscience. 2023. PMID: 36796752 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking and RSK activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jul;23(14):4796-804. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.14.4796-4804.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12832467 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding protein phosphorylation during oocyte meiotic divisions using phosphoproteomics.Elife. 2025 Jul 17;13:RP104255. doi: 10.7554/eLife.104255. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40674131 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of the effects of Rck2p mutants on Pbs2pDD-induced toxicity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identify a MAP kinase docking motif, and unexpected functional inactivation due to acidic substitution of T379.Mol Genet Genomics. 2004 Mar;271(2):208-19. doi: 10.1007/s00438-003-0972-6. Epub 2004 Jan 21. Mol Genet Genomics. 2004. PMID: 14735355
-
Signalling specificity of Ser/Thr protein kinases through docking-site-mediated interactions.Biochem J. 2003 May 15;372(Pt 1):1-13. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021641. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12600273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrieu A, Brassac T, Galas S, Fisher D, Labbe JC, Doree M. The polo-like kinase plx1 is a component of the MPF amplification loop at the G2/M-phase transition of the cell cycle in Xenopus eggs. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:1751–1757. - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C, Broek D, Wigler M. RAS proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985;43:615–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

