A nuclear protein involved in apoptotic-like DNA degradation in Stylonychia: implications for similar mechanisms in differentiating and starved cells
- PMID: 10473642
- PMCID: PMC25544
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.9.3003
A nuclear protein involved in apoptotic-like DNA degradation in Stylonychia: implications for similar mechanisms in differentiating and starved cells
Abstract
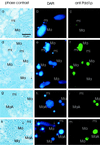
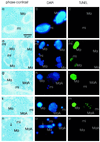
Ciliates are unicellular eukaryotic organisms containing two types of nuclei: macronuclei and micronuclei. After the sexual pathway takes place, a new macronucleus is formed from a zygote nucleus, whereas the old macronucleus is degraded and resorbed. In the course of macronuclear differentiation, polytene chromosomes are synthesized that become degraded again after some hours. Most of the DNA is eliminated, and the remaining DNA is fragmented into small DNA molecules that are amplified to a high copy number in the new macronucleus. The protein Pdd1p (programmed DNA degradation protein 1) from Tetrahymena has been shown to be present in macronuclear anlagen in the DNA degradation stage and also in the old macronuclei, which are resorbed during the formation of the new macronucleus. In this study the identification and localization of a Pdd1p homologous protein in Stylonychia (Spdd1p) is described. Spdd1p is localized in the precursor nuclei in the DNA elimination stage and in the old macronuclei during their degradation, but also in macronuclei and micronuclei of starved cells. In all of these nuclei, apoptotic-like DNA breakdown was detected. These data suggest that Spdd1p is a general factor involved in programmed DNA degradation in Stylonychia.
Figures

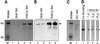


Similar articles
-
The formation of new nucleoli during macronuclear development of the hypotrichous ciliate Stylonychia lemnae visualized by in situ hybridization.Chromosome Res. 1997 Aug;5(5):333-5. doi: 10.1023/B:CHRO.0000038764.83094.aa. Chromosome Res. 1997. PMID: 9292238
-
Programmed nuclear death: apoptotic-like degradation of specific nuclei in conjugating Tetrahymena.Dev Biol. 1992 Dec;154(2):419-32. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90080-z. Dev Biol. 1992. PMID: 1426647
-
Pdd1p associates with germline-restricted chromatin and a second novel anlagen-enriched protein in developmentally programmed DNA elimination structures.Development. 1997 Nov;124(22):4537-45. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.22.4537. Development. 1997. PMID: 9409671
-
Biogenesis of Developmental Master Regulatory 27nt-RNAs in Stylonychia-Can Coding RNA Turn into Non-Coding?Genes (Basel). 2019 Nov 18;10(11):940. doi: 10.3390/genes10110940. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31752243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unusual features of non-dividing somatic macronuclei in the ciliate class Karyorelictea.Eur J Protistol. 2017 Oct;61(Pt B):399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.ejop.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 22. Eur J Protistol. 2017. PMID: 28673471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial and temporal plasticity of chromatin during programmed DNA-reorganization in Stylonychia macronuclear development.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2008 Oct 27;1(1):3. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-1-3. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2008. PMID: 19014664 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond transcriptional silencing: is methylcytosine a widely conserved eukaryotic DNA elimination mechanism?Bioessays. 2014 Apr;36(4):346-52. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300123. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Bioessays. 2014. PMID: 24519896 Free PMC article.
-
A PIWI homolog is one of the proteins expressed exclusively during macronuclear development in the ciliate Stylonychia lemnae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Oct 15;30(20):4380-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf579. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12384584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adl SM, Berger JD. Commitment to division in ciliate cell cycles. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1996;43:77–86. - PubMed
-
- Ammermann D, Steinbrück G, von Berger L, Hennig W. The development of the macronucleus in the ciliated protozoan Stylonychia mytilus. Chromosoma. 1974;45:401–429. - PubMed
-
- Berger JD, Ching AS. Commitment to division in Paramecium: effect of nutrient level on the macronuclear DNA increment. Exp Cell Res. 1989;182:90–104. - PubMed
-
- Callebaut I, Courvalin J-C, Wormann HJ, Mornon J-P. Hydrophobic cluster analysis reveals a third chromodomain in the Tetrahymena Pdd1p protein of the chromo superfamily. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;235:103–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

