An expanded peripheral T cell population to a cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)-defined, melanocyte-specific antigen in metastatic melanoma patients impacts on generation of peptide-specific CTLs but does not overcome tumor escape from immune surveillance in metastatic lesions
- PMID: 10477550
- PMCID: PMC2195616
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.190.5.651
An expanded peripheral T cell population to a cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)-defined, melanocyte-specific antigen in metastatic melanoma patients impacts on generation of peptide-specific CTLs but does not overcome tumor escape from immune surveillance in metastatic lesions
Abstract
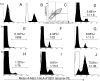
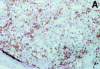
It is not known if immune response to T cell-defined human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I-restricted melanoma antigens leads to an expanded peripheral pool of T cells in all patients, affects cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) generation, and correlates with anti-tumor response in metastatic lesions. To this end, a limiting dilution analysis technique was developed that allowed us to evaluate the same frequency of peptide-specific T cells as by staining T cells with HLA-peptide tetrameric complexes. In four out of nine patients, Melan-A/Mart-1(27-35)-specific CTL precursors (CTLp) were >/=1/2,000 peripheral blood lymphocytes and found mostly or only in the CD45RO(+) memory T cell subset. In the remaining five patients, a low (<1/40,000) peptide-specific CTLp frequency was measured, and the precursors were only in the CD45RA(+) naive T cell subset. Evaluation of CTL effector frequency after bulk culture indicated that peptide-specific CTLs could be activated in all patients by using professional antigen-presenting cells as dendritic cells, but CTLp frequency determined the kinetics of generation of specificity and the final number of effectors as evaluated by both limiting dilution analysis and staining with HLA-A*0201-Melan-A/Mart-1 tetrameric complexes. Immunohistochemical analysis of 26 neoplastic lesions from the nine patients indicated absence of tumor regression in most instances, even in patients with an expanded peripheral T cell pool to Melan-A/Mart-1 and whose neoplastic lesions contained a high frequency of tetramer-positive Melan-A/Mart-1-specific T cells. Furthermore, frequent lack of a "brisk" or "nonbrisk" CD3(+)CD8(+) T cell infiltrate or reduced/absent Melan-A/Mart-1 expression in several lesions and lack of HLA class I antigens were found in some instances. Thus, expansion of peripheral immune repertoire to Melan-A/Mart-1 takes place in some metastatic patients and leads to enhanced CTL induction after antigen-presenting cell-mediated selection, but, in most metastatic lesions, it does not overcome tumor escape from immune surveillance.
Figures











References
-
- Clark W.H., Jr., Elder D.E., Guerry D., IV, Braitman L.E., Trock B.J., Schultz D., Synnestvedt M., Halpern A.C. Model predicting survival in stage I melanoma based on tumor progression. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989;81:1893–1904. - PubMed
-
- Mihm M., Clemente C., Cascinelli N. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in lymph node melanoma metastasesa histopathologic prognostic indicator and an expression of local immune response. Lab. Invest. 1996;74:43–47. - PubMed
-
- Sensi M.L., Parmiani G. Analysis of TCR usage in human tumorsa new tool for assessing tumor-specific immune responses. Immunol. Today. 1995;16:588–595. - PubMed
-
- Rivoltini L., Kawakami Y., Sakaguchi K., Southwood S., Sette A., Robbins P.F., Marincola F.M., Salgaller M.L., Yannelli J.R., Appella E. Induction of tumor-reactive CTL from peripheral blood and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of melanoma patients by in-vitro stimulation with an immunodominant peptide of the human melanoma antigen MART-1. J. Immunol. 1995;154:2257–2265. - PubMed
-
- Salgaller M.L., Afshar A., Marincola F.M., Rivoltini L., Kawakami Y., Rosenberg S.A. Recognition of multiple epitopes in the human melanoma antigen gp100 by peripheral blood lymphocytes stimulated in-vitro with synthetic peptides. Cancer Res. 1995;55:4972–4979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

