Differential expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4/5 in the adult rat spinal cord: regulation by the glutamate receptor agonist kainic acid
- PMID: 10479679
- PMCID: PMC6782449
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-18-07757.1999
Differential expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4/5 in the adult rat spinal cord: regulation by the glutamate receptor agonist kainic acid
Abstract
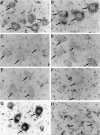
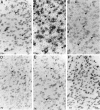
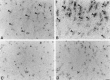
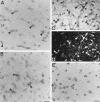
Previous in vitro studies indicate that select members of the neurotrophin gene family, namely brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5), contribute to survival and differentiation of spinal cord motoneurons. To investigate the potential roles of these factors in the adult spinal cord, we examined their cellular localization and regulation after systemic exposure to an excitotoxic stimulus, kainic acid (KA). Of the neurotrophins examined, NT-4/5 mRNA was most robustly expressed in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the normal adult rat, including expression by neurons throughout the gray matter, and in a subpopulation of white and gray matter glia. Both BDNF and NT-3 mRNAs were also densely expressed by alpha motoneurons of lamina IX, but were detected at lower levels elsewhere in the gray matter. NT-3 mRNA was additionally expressed by spinal cord glia, but was less widespread compared to NT-4/5. In response to systemic administration of KA, NT-4/5 and BDNF mRNAs were dramatically upregulated in a spatially and temporally restricted fashion, whereas levels of NT-3 mRNA were unchanged. These results provide strong in vivo evidence to support the idea that BDNF, NT-3, and in particular, NT-4/5, play a role in the normal function of the adult spinal cord. Furthermore, our results indicate that the actions of BDNF and NT-4/5 participate in the response of the cord to excitotoxic stimuli, and that those of NT-4/5 and NT-3 include both neurons and glia.
Figures
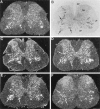
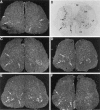
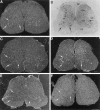

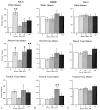
References
-
- Aloe L. Intracerebral pretreatment with nerve growth factor prevents irreversible brain lesions in neonatal rats injected with ibotenic acid. Biotechnology. 1987;5:1085–1086.
-
- Barres BA, Koroshetz WJ, Swartz KJ, Chun LL, Corey DP. Ion channel expression by white matter glia: the O-2A glial progenitor cell. Neuron. 1990;4:507–524. - PubMed
-
- Barres BA, Raff MC, Gaese F, Bartke I, Dechant G, Barde Y-A. A crucial role for neurotrophin-3 in oligodendrocyte development. Nature. 1994;367:371–375. - PubMed
-
- BDNF Study Group (Phase III) A controlled trial of recombinant methionyl human BDNF in ALS. Neurology. 1999;52:1427–1433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
