Tetanic stimulation leads to increased accumulation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II via dendritic protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 10479685
- PMCID: PMC6782482
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-18-07823.1999
Tetanic stimulation leads to increased accumulation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II via dendritic protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
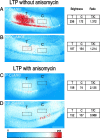
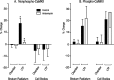
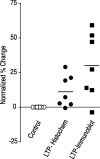
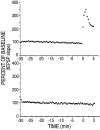
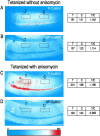
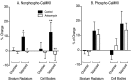
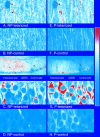
mRNA for the alpha-subunit of CaMKII is abundant in dendrites of neurons in the forebrain (Steward, 1997). Here we show that tetanic stimulation of the Schaffer collateral pathway causes an increase in the concentration of alpha-CaMKII in the dendrites of postsynaptic neurons. The increase is blocked by anisomycin and is detected by both quantitative immunoblot and semiquantitative immunocytochemistry. The increase in dendritic alpha-CaMKII can be measured 100-200 micrometer away from the neuronal cell bodies as early as 5 min after a tetanus. Transport mechanisms for macromolecules from neuronal cell bodies are not fast enough to account for this rapid increase in distal portions of the dendrites. Therefore, we conclude that dendritic protein synthesis must produce a portion of the newly accumulated CaMKII. The increase in concentration of dendritic CaMKII after tetanus, together with the previously demonstrated increase in autophosphorylated CaMKII (Ouyang et al., 1997), will produce a prolonged increase in steady-state kinase activity in the dendrites, potentially influencing mechanisms of synaptic plasticity that are controlled through phosphorylation by CaMKII.
Figures
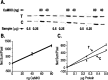
References
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaMKII during long term potentiation. Science. 1997;276:2042–2045. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MK, Erondu NE, Kennedy MB. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that is highly concentrated in brain. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:12735–12744. - PubMed
-
- Benson DL, Isackson PJ, Gall CM, Jones EG. Contrasting patterns in the localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase and Ca2+/calmodulin protein kinase gene expression in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1992;46:825–849. - PubMed
-
- Brady S, Lasek R. Axonal transport: a cell-biological method for studying proteins that associate with the cytoskeleton. In: Wilson L, editor. Methods in cell biology. Academic; New York: 1982. pp. 365–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
