Role of the alkyl hydroperoxide reductase (ahpCF) gene in oxidative stress defense of the obligate Anaerobe bacteroides fragilis
- PMID: 10482511
- PMCID: PMC94090
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.18.5701-5710.1999
Role of the alkyl hydroperoxide reductase (ahpCF) gene in oxidative stress defense of the obligate Anaerobe bacteroides fragilis
Abstract
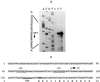
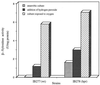
In this study we report the identification and role of the alkyl hydroperoxide reductase (ahp) gene in Bacteroides fragilis. The two components of ahp, ahpC, and ahpF, are organized in an operon, and the deduced amino acid sequences revealed that B. fragilis AhpCF shares approximately 60% identity to orthologues in other gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Northern blot hybridization analysis of total RNA showed that the ahpCF genes were transcribed as a polycistronic 2.4-kb mRNA and that ahpC also was present as a 0.6-kb monocistronic mRNA. ahpC and ahpCF mRNAs were induced approximately 60-fold following H(2)O(2) treatment or oxygen exposure of the parent strain but were constitutive in a peroxide-resistant strain. Further investigation using an ahpCF'::beta-xylosidase gene transcriptional fusion confirmed that ahpCF had lost normal regulation in the peroxide-resistant strain compared to the parent. The ahpCF mutant was more sensitive to growth inhibition and mutagenesis by organic peroxides than the parent strain, as determined by disk inhibition assays and the frequency of mutation to fusidic acid resistance. This finding suggests that the ahp genes play an important role in peroxide resistance in B. fragilis. Under anaerobic conditions, we observed increases in the number of spontaneous fusidic acid-resistant mutants of five- and sevenfold in ahpCF and ahpF strain backgrounds, respectively, and eightfold in the ahpCF katB double mutant strain compared to the parent and katB strains. In addition, ahpCF, ahpF, and ahpCF katB mutants were slightly more sensitive to oxygen exposure than the parent strain. Moreover, the isolation of a strain with enhanced aerotolerance and high-level resistance to alkyl hydroperoxides from an ahpCF katB parent suggests that the physiological responses to peroxide toxicity and to the toxic effects of molecular oxygen are overlapping and complex in this obligate anaerobe.
Figures


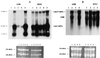

Similar articles
-
The redox-sensitive transcriptional activator OxyR regulates the peroxide response regulon in the obligate anaerobe Bacteroides fragilis.J Bacteriol. 2000 Sep;182(18):5059-69. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.18.5059-5069.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10960088 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of the Bacillus subtilis alkyl hydroperoxide reductase (ahpCF) operon reveals compensatory interactions among hydrogen peroxide stress genes.J Bacteriol. 1996 Nov;178(22):6579-86. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.22.6579-6586.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8932315 Free PMC article.
-
Flavin-dependent alkyl hydroperoxide reductase from Salmonella typhimurium. 1. Purification and enzymatic activities of overexpressed AhpF and AhpC proteins.Biochemistry. 1996 Jan 9;35(1):56-64. doi: 10.1021/bi951887s. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8555198
-
Characterization of oxidative stress-induced cgahp, a gene coding for alkyl hydroperoxide reductase, from industrial importance Corynebacterium glutamicum.Biotechnol Lett. 2023 Oct;45(10):1309-1326. doi: 10.1007/s10529-023-03421-8. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Biotechnol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37606753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tightly controlled response to oxidative stress; an important factor in the tolerance of Bacteroides fragilis.Res Microbiol. 2021 Mar;172(2):103798. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2021.103798. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Res Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33485914 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the primary starch utilization operon in the obligate anaerobe Bacteroides fragilis: Regulation by carbon source and oxygen.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jul;188(13):4663-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.00125-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16788175 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione and catalase provide overlapping defenses for protection against respiration-generated hydrogen peroxide in Haemophilus influenzae.J Bacteriol. 2003 Sep;185(18):5555-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.18.5555-5562.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12949108 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial protein signals are associated with Crohn's disease.Gut. 2014 Oct;63(10):1566-77. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303786. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Gut. 2014. PMID: 24436141 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Mediating Environmental Biofilm Formation by Legionella pneumophila.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Feb 27;8:38. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00038. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29535972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tiny but Mighty: Small RNAs-The Micromanagers of Bacterial Survival, Virulence, and Host-Pathogen Interactions.Noncoding RNA. 2025 May 5;11(3):36. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11030036. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40407594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altuvia S, Almirón M, Huisman G, Kolter R, Storz G. The dps promoter is activated by OxyR during growth and by IHF and ςs in stationary phase. Mol Microbiol. 1994;13:265–272. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons Inc.; 1987.
-
- Calzi M L, Poole L B. Requirement for the two AhpF cystine disulfide centers in catalysis of peroxide reduction by alkyl hydroperoxide reductase. Biochemistry. 1997;36:13357–13364. - PubMed
-
- Chae H Z, Rhee S G. A thiol-specific antioxidant and sequence homology to various proteins of unknown function. Biofactors. 1994;4:177–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

