Functional analysis of the interaction between VPg-proteinase (NIa) and RNA polymerase (NIb) of tobacco etch potyvirus, using conditional and suppressor mutants
- PMID: 10482627
- PMCID: PMC112894
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.10.8732-8740.1999
Functional analysis of the interaction between VPg-proteinase (NIa) and RNA polymerase (NIb) of tobacco etch potyvirus, using conditional and suppressor mutants
Abstract
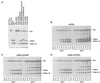
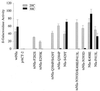
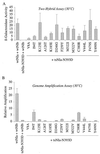
The tobacco etch potyvirus (TEV) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (NIb) has been shown to interact with the proteinase domain of the VPg-proteinase (NIa). To investigate the significance of this interaction, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae two-hybrid assay was used to isolate conditional NIa mutant proteins with temperature-sensitive (ts) defects in interacting with NIb. Thirty-six unique tsNIa mutants with substitutions affecting the proteinase domain were recovered. Most of the mutants coded for proteins with little or no proteolytic activity at permissive and nonpermissive temperatures. However, three mutant proteins retained proteolytic activity at both temperatures and, in two cases (tsNIa-Q384P and tsNIa-N393D), the mutations responsible for the ts interaction phenotype could be mapped to single positions. One of the mutations (N393D) conferred a ts-genome-amplification phenotype when it was placed in a recombinant TEV strain. Suppressor NIb mutants that restored interaction with the tsNIa-N393D protein at the restrictive temperature were recovered by a two-hybrid selection system. Although most of the suppressor mutants failed to stimulate amplification of genomes encoding the tsNIa-N393D protein, two suppressors (NIb-I94T and NIb-C380R) stimulated amplification of virus containing the N393D substitution by approximately sevenfold. These results support the hypothesis that interaction between NIa and NIb is important during TEV genome replication.
Figures


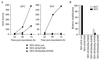

References
-
- Allaire M, Chernaia M M, Malcolm B A, James M N. Picornaviral 3C cysteine proteinases have a fold similar to chymotrypsin-like serine proteinases. Nature. 1994;369:72–76. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Short protocols in molecular biology. 3rd ed. New York, N.Y: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.; 1995.
-
- Cadwell R, Joyce G. Randomization of genes by PCR mutagenesis. PCR Methods Appl. 1992;2:28–33. - PubMed
-
- Carrington J C, Dougherty W G. Processing of the tobacco etch virus 49K protease requires autoproteolysis. Virology. 1987;160:355–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

