Arabidopsis mutants lacking the 43- and 54-kilodalton subunits of the chloroplast signal recognition particle have distinct phenotypes
- PMID: 10482661
- PMCID: PMC59390
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.121.1.61
Arabidopsis mutants lacking the 43- and 54-kilodalton subunits of the chloroplast signal recognition particle have distinct phenotypes
Abstract
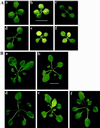
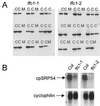
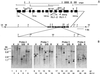
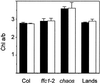
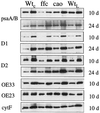
The chloroplast signal recognition particle (cpSRP) is a protein complex consisting of 54- and 43-kD subunits encoded by the fifty-four chloroplast, which encodes cpSRP54 (ffc), and chaos (cao) loci, respectively. Two new null alleles in the ffc locus have been identified. ffc1-1 is caused by a stop codon in exon 10, while ffc1-2 has a large DNA insertion in intron 8. ffc mutants have yellow first true leaves that subsequently become green. The reaction center proteins D1, D2, and psaA/B, as well as seven different light-harvesting chlorophyll proteins (LHCPs), were found at reduced levels in the young ffc leaves but at wild-type levels in the older leaves. The abundance of the two types of LHCP was unaffected by the mutation, while two others were increased in the absence of cpSRP54. Null mutants in the cao locus contain reduced levels of the same subset of LHCP proteins as ffc mutants, but are distinguishable in four ways: young leaves are greener, the chlorophyll a/b ratio is elevated, levels of reaction center proteins are normal, and there is no recovery in the level of LHCPs in the adult plant. The data suggest that cpSRP54 and cpSRP43 have some nonoverlapping roles and that alternative transport pathways can compensate for the absence of a functional cpSRP.
Figures


References
-
- Brock IW, Mills JD, Robinson D, Robinson C. The delta pH-driven, ATP-independent protein translocation mechanism in the chloroplast thylakoid membrane: kinetics and energetics. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:1657–1662. - PubMed
-
- Cline K, Ettinger WF, Theg SM. Protein-specific energy requirements for protein transport across or into thylakoid membranes: two lumenal proteins are transported in the absence of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:2688–2696. - PubMed
-
- Cline K, Henry R. Import and routing of nucleus-encoded chloroplast proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996;12:1–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

