UTP-preferring P2 receptor mediates inhibition of sodium transport in porcine thyroid epithelial cells
- PMID: 10482908
- PMCID: PMC1566178
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702733
UTP-preferring P2 receptor mediates inhibition of sodium transport in porcine thyroid epithelial cells
Abstract
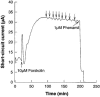
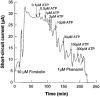
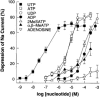
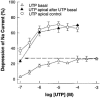
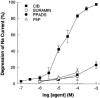
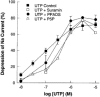
1. The effects of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP), uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP) and analogues on forskolin-stimulated absorption of Na+ by porcine thyroid epithelial cells were analysed in cultures grown as confluent monolayers on permeable supports in Transwell Ussing chambers. 2. 85% of the forskolin (10 microM)-stimulated short-circuit current was inhibited by phenamil (1 microM), which is a selective antagonist for epithelial type Na+ channels. 3. Phenamil-sensitive current was inhibited in a dose dependent manner by nucleotides added to the apical compartment of Ussing chambers. In contrast, the phenamil-resistant current, previously shown to represent anion secretion, was unaffected by nucleotides. 4. The order of potency (with EC50 values given in microM) was UTP (0.08)>>ATP (6.3)=uridine 5'-diphosphate (UDP) (6. 6)>2methyl-thio-adenosine-5'-triphosphate (2MeSATP) (84.5)>adenosine 5'-diphosphate (ADP) (147.8)>alpha,beta-methylene ATP (>150)>>adenosine (>1000). 5. P2 receptors mediating inhibition of sodium absorption were present on the apical membrane of the cells since addition of UTP (1-1000 microM) to the basal compartment of the Ussing chambers had little effect while subsequent addition to the apical compartment produced a normal response. 6. Cibachron blue (Reactive blue 2) (1-100 microM), an antagonist at some P2 receptor subtypes, inhibited phenamil sensitive current in a dose dependent manner with half maximal inhibition occurring at 14.25 microM. 7. Suramin (100 microM), pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2', 4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS) (100 microM) and pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (P5P) (100 microM) showed only slight competitive antagonism against the response to UTP. 8 These results indicate that a UTP-preferring P2 receptor located on the apical membrane of thyroid epithelial cells mediates inhibition of Na+ absorption.
Figures
References
-
- AL-AWQATI Q. Regulation of ion channels by ABC transporters that secrete ATP. Science. 1995;269:805–806. - PubMed
-
- ARMSTRONG J., MATAINAHO T., CRAGOE E.J., JR, HUXHAM G.J., BOURKE J.R., MANLEY S.W. Bidirectional ion transport in thyroid: secretion of anions by cultured porcine thyroid cell monolayers which absorb sodium. Am. J. Physiol. 1992;262:E40–E45. - PubMed
-
- BENNETT W.D., OLIVIER K.N., ZEMAN K.L., HOHNEKER K.W., BOUCHER R.C., KNOWLES M.R. Effect of uridine 5′-triphosphate plus amiloride on mucociliary clearance in adult cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996;153:1796–1801. - PubMed
-
- BOURKE J.R., ABEL K.C., HUXHAM G.J., SAND O., MANLEY S.W. Sodium channel heterogeneity in the apical membrane of thyroid epithelial cells. J. Endocrinol. 1996;149:101–108. - PubMed
-
- BOURKE J.R., CARSELDINE K.L., FERRIS S.H., HUXHAM G.J., MANLEY S.W. Changes in membrane potential of cultured porcine and human thyroid cells in response to thyrotrophin and other agents. J. Endocrinol. 1981;88:187–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

