Eukaliuric diuresis and natriuresis in response to the KATP channel blocker U37883A: micropuncture studies on the tubular site of action
- PMID: 10482911
- PMCID: PMC1566186
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702742
Eukaliuric diuresis and natriuresis in response to the KATP channel blocker U37883A: micropuncture studies on the tubular site of action
Abstract
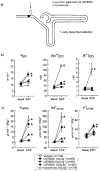
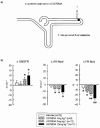
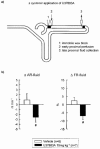
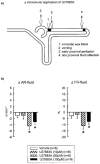
1. Systemic application of U37883A, a blocker of ATP sensitive potassium (KATP) channels, elicits diuresis and natriuresis without significantly altering urinary potassium excretion. 2. To elucidate tubular sites of action upstream to the distal nephron, micropuncture experiments were performed in nephrons with superficial glomeruli of anaesthetized Munich-Wistar-Frömter rats during systemic application of U37883A (1, 5 or 15 mg kg-1 i.v.). 3. The observed eukaliuric diuresis and natriuresis in response to U37883A at 15 mg kg-1 was accompanied by an increase in early distal tubular flow rate (VED) from 10 - 18 nl min(-1) reflecting a reduction in fractional reabsorption of fluid up to this site (FR-fluid) of 13%. The latter proposed an effect on water-permeable segments such as the proximal tubule which could fully account for the observed reduction in fractional reabsorption of Na+ up to the early distal tubule (FR-Na+) of 8% and the increase in early distal tubular Na+ concentration ([Na+]ED) from 35 - 51 mM whereas [K+]ED was left unaltered. 4. In comparison, furosemide (3 mg kg-1 i.v.), which acts in the water-impermeable thick ascending limb, elicited diuresis, natriuresis and kaliuresis which were associated with a fall in FR-Na+ of 10% with no change in FR-fluid, and a rise in [Na+]ED from 42 - 117 mM and [K+]ED from 1.2 - 5.7 mM with no change in VED. 5. Direct late proximal tubular fluid collections confirmed a significant inhibition of fluid reabsorption in proximal convoluted tubule in response to systemic application of U37883A. 6. These findings suggest that the diuretic and natriuretic effect upstream to the distal tubule in response to systemic application of U37883A involves actions on water-permeable segments such as the proximal convoluted tubule.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium reabsorption in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop: effect of potassium channel blockade in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Jul;130(6):1255-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703429. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10903963 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaliuric natriuresis and diuresis in response to disprocynium24: studies on the tubular site of action.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998 Aug;358(2):238-44. doi: 10.1007/pl00005248. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9750010
-
Potential role of luminal potassium in tubuloglomerular feedback.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997 Dec;8(12):1831-7. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V8121831. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997. PMID: 9402084
-
Magnesium and potassium-sparing diuretics.Magnesium. 1986;5(5-6):282-92. Magnesium. 1986. PMID: 3543514 Review.
-
The site of action of furosemide.Pharmacol Res. 1998 May;37(5):409-19. doi: 10.1006/phrs.1998.0311. Pharmacol Res. 1998. PMID: 9642037 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo stimulation of AMP-activated protein kinase enhanced tubuloglomerular feedback but reduced tubular sodium transport during high dietary NaCl intake.Pflugers Arch. 2010 Jun;460(1):187-96. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0803-7. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 20349193
-
Sodium reabsorption in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop: effect of potassium channel blockade in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Jul;130(6):1255-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703429. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10903963 Free PMC article.
-
Micropuncturing the nephron.Pflugers Arch. 2009 May;458(1):189-201. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0581-7. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 18752000 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BECK J.S., HURST A.M., LAPOINTE J.-Y., LAPRADE R. Regulation of basolateral potassium channels in proximal tubule studied during continuous microperfusion. Am. J. Physiol. 1993;264:F496–F501. - PubMed
-
- BLEICH M., SCHLATTER E., GREGER R. The luminal K+ channel of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Pfluegers. Arch. 1990;415:449–460. - PubMed
-
- CLARK M.A., HUMPHREY S.J., SMITH M.P., LUDENS J.H. Unique natriuretic properties of the ATP-sensitive K+-channel blocker glyburide in conscious rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993;265:933–937. - PubMed
-
- FERRIER C.P., KURTZ A., LEHNER P., SHAW S.G., PUSTERLA C., SAXENHOFER H., WEIDMANN P. Stimulation of renin secretion by potassium-channel activation with cromakalim. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1989;36:443–447. - PubMed
-
- GUILLEMARE E., HONORE E., DE WEILLE J., FOSSET M., LAZDUNSKI M., MEISHERI K. Functional receptors in Xenopus oocytes for U-37883A, a novel ATP-sensitive K+ channel blocker: Comparison with rat insulinoma cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994;46:139–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

