In vivo B1 kinin-receptor upregulation. Evidence for involvement of protein kinases and nuclear factor kappaB pathways
- PMID: 10482916
- PMCID: PMC1566166
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702715
In vivo B1 kinin-receptor upregulation. Evidence for involvement of protein kinases and nuclear factor kappaB pathways
Abstract
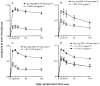
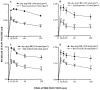
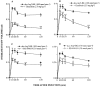
1. Intradermal (i.d.) injection of cytokines, IL-1beta and TNFalpha (5 ng, 60 and 30 min prior) produces a rapid onset up-regulation of des-Arg9-BK-mediated rat paw oedema. Here we analyse the mechanisms involved in des-Arg9-BK-induced oedema in animals pre-treated with IL-1beta or TNFalpha. 2. Co-injection of anti-IL-1beta, anti-TNFalpha and anti-IL-8 (50 ng) significantly inhibited des-Arg9-BK-induced oedema in animals pre-treated with IL-1beta (65, 37 and 42%) or TNFalpha (39, 64, 25%). IL-1 receptor antagonist (IRA, 100 microg) or IL-10 (10 ng) inhibited the oedema caused by des-Arg9-BK, in rats that had received either IL-1beta (67 and 63%) or TNFalpha (46 and 35%). 3. Co-injection of the PKC inhibitors, staurosporine (10 nmol) or RO 318220 (30 nmol) inhibited des-Arg9-BK-induced paw oedema (44 and 42% for IL-1beta and, 53 and 30% for TNFalpha, respectively). Genistein (tyrosine kinase inhibitor, 2.5 mg kg-1, s.c.) or PD 098059 (MAP-kinase inhibitor, 30 nmol) produced marked inhibition of des-Arg9-BK-induced oedema (58 and 39% for IL-1beta and 31 and 35% for TNFalpha respectively). 4. The NF-kappaB inhibitors TLCK (2 mg kg-1, i.p.) and PDCT (100 mg kg-1, i.p.) significantly inhibited the oedema of des-Arg9-BK in IL-1beta (27 and 83%) or TNFalpha (28 and 80%) pre-treated animals. 5. It is concluded that up-regulation of B1 receptors modulated by IL-1beta or TNFalpha involves the release of other cytokines, activation of PKC and tyrosine kinase pathways, co-ordinated with the activation of MAP-kinase and nuclear factor kappaB, reinforcing the view that B1 receptors may exert a pivotal role in modulating chronic inflammatory processes.
Figures


References
-
- BARNES P.J., ADCOCK I.M. NF-κB: a pivotal role in asthma and a new target for therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1997;18:47–50. - PubMed
-
- BARNES P.J., KARIN M. Nuclear factor-κB–a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N. Eng. J. Med. 1997;336:1066–1071. - PubMed
-
- BHOOLA K.D., FIGUEROA C.D., WORTHY K. Biorregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol. Rev. 1992;44:1–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

