PKCbetaI mediates the inhibition of P2Y receptor-induced inositol phosphate formation in endothelial cells
- PMID: 10482923
- PMCID: PMC1566172
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702727
PKCbetaI mediates the inhibition of P2Y receptor-induced inositol phosphate formation in endothelial cells
Abstract
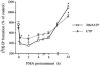
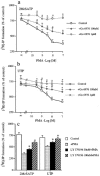
1. Bovine pulmonary artery endothelium (CPAE) expresses phospholipase C (PLC)-linked P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptors, for them 2-methylthio-ATP (2MeSATP) and UTP are respective agonists. Here, we have investigated the particular protein kinase C (PKC) isoform(s) responsible for the inhibition of P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptor-evoked inositol phosphate (IP) formation by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). 2. Although short-term (20 min) pretreatment of cells with PMA attenuated 2MeSATP- and UTP-induced phosphoinositide (PI) breakdown, this inhibition was lost after 15 h. Preincubation with PMA for 24 h, on the contrary, potentiated 2MeSATP and UTP responses. The IP formation stimulated by NaF was unaltered by PMA pretreatment. 3. Western blot analysis showed that treatment of CPAE with PMA resulted in a rapid translocation of PKC isoform betaI, epsilon and mu, but not lambda, from the cytosol to the membrane fraction. 4. Pretreatment of the selective PKC inhibitor Ro 31-8220 attenuated the inhibitory effect of PMA on IP formation. Go 6976 (an inhibitor of conventional PKCalpha, beta and gamma) and LY 379196 (a selective PKCbeta inhibitor) also dose-dependently inhibited the PMA-mediated desensitization. 5. Transfection of PKCbeta-specific antisense oligonucleotide reduced PKCbetaI protein level and inhibited PMA-mediated PI reduction. 6. RT - PCR analysis showed that PMA treatment for 4 - 24 h up-regulated P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptors at the mRNA levels. 7. These results suggest that PKCbetaI may exert a negative feedback regulation on endothelial P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptor-mediated PI turnover. The down-regulation of PKCbetaI and enhanced P2Y receptor expression together might contribute to the late PI enhancing effect of PMA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C epsilon-dependent pathway of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase activation by P2Y1 and P2Y2 purinoceptors that activate cytosolic phospholipase A2 in endothelial cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 May 28;373(1):101-10. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00238-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10408256
-
Regulation of brain capillary endothelial cells by P2Y receptors coupled to Ca2+, phospholipase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Nov;122(5):935-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701453. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9384512 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of signaling pathways of P2Y and P2U purinoceptors in bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;28(2):192-9. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199608000-00003. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8856473
-
Role of protein kinase C in the regulation of prostaglandin synthesis in human endothelium.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;6(3):315-25. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/6.3.315. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992. PMID: 1540395
-
Endothelial P2-purinoceptors: subtypes and signal transduction.J Auton Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;16(6):353-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1996.tb00052.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 9131415 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of P2Y receptor-activated signal transduction pathways in G protein-dependent signalling networks.Purinergic Signal. 2006 Sep;2(3):451-69. doi: 10.1007/s11302-006-9008-0. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Purinergic Signal. 2006. PMID: 18404483 Free PMC article.
-
ADP-sensitive purinoceptors induce steroidogenesis via adenylyl cyclase activation in bovine adrenocortical fasciculata cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Sep;137(2):177-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704847. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12208774 Free PMC article.
-
Two subtypes of G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors, P2Y(1) and P2Y(2) are involved in calcium signalling in glioma C6 cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jan;132(2):393-402. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703843. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11159687 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of P2Y(11) receptor-mediated signalling to phospholipase C and adenylyl cyclase by protein kinase C in HL-60 promyelocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Oct;131(3):489-97. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703581. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11015299 Free PMC article.
-
Desensitization of endothelial P2Y1 receptors by PKC-dependent mechanisms in pressurized rat small mesenteric arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;158(6):1609-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00456.x. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19845669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BELTMAN J., MCCORMICK F., COOK S.J. The selective protein kinase C inhibitor, Ro 31-8220, inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) expression, induced c-Jun expression, and activates Jun N-terminal kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;171:27018–27024. - PubMed
-
- BOARDER M.R., HOURANI S.M. The regulation of vascular function by P2 receptors: multiple sites and multiple receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1998;19:99–107. - PubMed
-
- BOARDER M.R., WEISMAN G.A., TURNER J.T., WILKINSON G.F. G protein-coupled P2 purinoceptors: from molecular biology to functional responses. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995;16:133–139. - PubMed
-
- BOEYNAEMS J.-M., PEARSON J.D. P2 purinoceptors on vascular endothelial cells: physiological significance and transduction mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1990;11:34–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

