Carboxyl ester lipase activity in milk prevents fat-derived intestinal injury in neonatal mice
- PMID: 10484391
- PMCID: PMC2583025
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.1999.277.3.G653
Carboxyl ester lipase activity in milk prevents fat-derived intestinal injury in neonatal mice
Abstract
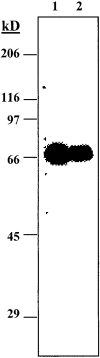
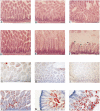
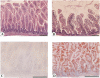
Carboxyl ester lipase (bile salt-stimulated lipase) is a pancreatic enzyme capable of hydrolyzing esters of cholesterol and fat-soluble vitamins. It also efficiently digests triglycerides (TG) into free fatty acids and glycerol and is abundant in the milk of humans and several other species. We used the mouse as a model to test the hypothesis that milk-derived carboxyl ester lipase (CEL) digests milk TG and that without its activity milk lipids and their digestion intermediates can disrupt the intestinal epithelium of neonates. CEL protein and enzymatic activity were shown to be abundant in mouse milk. After 24-h administration of the CEL-specific inhibitor, WAY-121,751-5, the small intestines of treated and control neonates were analyzed histologically for signs of fat malabsorption and injury to their villus epithelium. In vehicle-fed controls, TG were digested and absorbed in the duodenum and jejunum, whereas, in inhibitor-fed littermates, large intracellular neutral lipid droplets accumulated in enterocytes of the ileum, resulting in damage to the villus epithelium. Similar results were observed in neonates nursed by CEL knockout females compared with heterozygous controls. The results suggest that lack of CEL activity causes incomplete digestion of milk fat and lipid accumulation by enterocytes in the ileum of neonatal mice.
Figures
References
-
- Alemi B, Hamosh M, Scanlon JW, Salzman-Mann C, Hamosh P. Fat digestion in very low-birth-weight infants: effect of addition of human milk to low-birth-weight formula. Pediatrics. 1981;68:484–489. - PubMed
-
- Barlow B, Santulli TV, Heird WC, Pitt J, Blanc WA, Schullinger JN. An experimental study of acute neonatal enterocolitis—the importance of breast milk. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1974;9:587–595. - PubMed
-
- Bennett-Clark S, Lawergren B, Martin J. Regional intestinal absorptive capacities for triolein: an alternative to markers. Am. J. Physiol. 1973;225:574–585. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia AM, Feddersen RM, Musemeche CA. The role of luminal nutrients in intestinal injury from mesenteric reperfusion and platelet-activating factor in the developing rat. J. Surg. Res. 1996;63:152–156. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia AM, Ramos CT, Scott SM, Musemeche CA. Developmental susceptibility to intestinal injury by platelet-activating factor in the newborn rat. J. Invest. Surg. 1996;9:351–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

