Inhibition of apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion prevents inflammation
- PMID: 10487768
- PMCID: PMC408540
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI6974
Inhibition of apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion prevents inflammation
Abstract
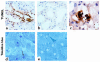
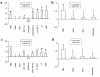
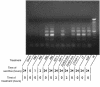
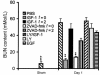
Ischemia followed by reperfusion leads to severe organ injury and dysfunction. Inflammation is considered to be the most important cause of tissue injury in organs subjected to ischemia. The mechanism that triggers inflammation and organ injury after ischemia remains to be elucidated, although different causes have been postulated. We investigated the role of apoptosis in the induction of inflammation and organ damage after renal ischemia. Using a murine model, we demonstrate a relationship between apoptosis and subsequent inflammation. At the time of reperfusion, administration of the antiapoptotic agents IGF-1 and ZVAD-fmk (a caspase inactivator) prevented the early onset of not only renal apoptosis, but also inflammation and tissue injury. Conversely, when the antiapoptotic agents were administered after onset of apoptosis, these protective effects were completely abrogated. The presence of apoptosis was directly correlated with posttranslational processing of the endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide II (EMAP-II), which may explain apoptosis-induced influx and sequestration of leukocytes in the reperfused kidney. These results strongly suggest that apoptosis is a crucial event that can initiate reperfusion-induced inflammation and subsequent tissue injury. The newly described pathophysiological insights provide important opportunities to effectively prevent clinical manifestations of reperfusion injury in the kidney, and potentially in other organs.
Figures


References
-
- Nogae S, et al. Induction of apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion model of mouse kidney: possible involvement of Fas. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:620–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

