Molecular characterization of a Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli O113:H21 strain lacking eae responsible for a cluster of cases of hemolytic-uremic syndrome
- PMID: 10488206
- PMCID: PMC85566
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.10.3357-3361.1999
Molecular characterization of a Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli O113:H21 strain lacking eae responsible for a cluster of cases of hemolytic-uremic syndrome
Abstract
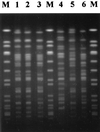
Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC) strains are a diverse group of organisms capable of causing severe gastrointestinal disease in humans. Within the STEC family, certain strains appear to have greater virulence for humans. STEC strains carrying eae and belonging to serogroup O157 or O111 have been responsible for the vast majority of outbreaks of STEC disease reported to date. Here we describe a STEC O113:H21 strain lacking eae that was responsible for a cluster of three cases of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. This strain produces a single Stx2-related toxin and adheres efficiently to Henle 407 cells.
Figures




References
-
- Banatvala N, Debeukelaer M M, Griffin P M, Barrett T J, Greene K D, Green J H, Wells J G. Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli O111 and associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome: a family outbreak. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996;15:1008–1011. - PubMed
-
- Barrett T J, Kaper J B, Jerse A E, Wachsmuth I K. Virulence factors in Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from humans and cattle. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:979–980. - PubMed
-
- Boudailliez B, Berquin P, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Ilef D, Cuvelier B, Capek I, Tribout B, Bingen E, Piussan C. Possible person-to-person transmission of Escherichia coli O111-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 1997;11:36–39. - PubMed
-
- Caprioli A, Luzzi I, Rosmini F, Resti C, Edefonti A, Perfumo F, Farina C, Goglio A, Gianviti A, Rizzone G. Communitywide outbreak of hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with non-O157 Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1994;169:208–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

