Conditioning method dramatically alters the role of amygdala in taste aversion learning
- PMID: 10489263
- PMCID: PMC311265
Conditioning method dramatically alters the role of amygdala in taste aversion learning
Erratum in
- Learn Mem 1999 Jan-Feb;6(1):62
Abstract
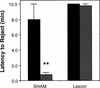
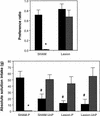
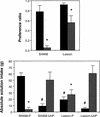
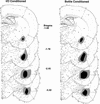
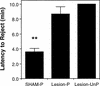
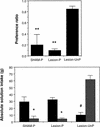
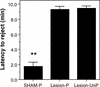
Although an important role for the amygdala in taste aversion learning has been suggested by work in a number of laboratories, results have been inconsistent and interpretations varied. The present series of studies reevaluated the role of the amygdala in taste aversion learning by examining the extent to which conditioning methods, testing methods and lesioning methods, influence whether amygdala lesions dramatically affect conditioned taste aversion (CTA) learning. Results indicated that when animals are conditioned with an intraoral (I/O) taste presentation, lesions of amygdala eliminate evidence of conditioning whether animals are tested intraorally or with a two-bottle solution presentation. Dramatic effects of amygdala lesions on CTA learning were seen whether lesions were made electrolytically or using an excitotoxin. In contrast, when animals were conditioned using bottle presentation of the taste, electrolytic lesions attenuated CTAs but did not eliminate them, and excitotoxic lesions had no effect. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that neural structures critical for CTA learning may differ depending on the extent to which the method of conditioned stimulus delivery incorporates a response component.
Figures


References
-
- Bermudez-Rattoni F, McGaugh JL. Insular cortex and amygdala lesions differentially affect acquisition on inhibitory avoidance and conditioned taste aversion. Brain Res. 1991;549:165–170. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein IL. Flavor aversion. In: Getchell TV, Doty RL, Bartoshuk LM, Snow JB, editors. Smell and taste in health and disease. New York, NY: Raven Press; 1991. pp. 417–428.
-
- Braun JJ, Lasiter PS, Kiefer SW. The gustatory neocortex of the rat. Physiol Psychol. 1982;10:13–45.
-
- Chambers KC. A neural model of conditioned taste aversions. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:373–385. - PubMed
-
- Dunn LT, Everitt BJ. Double dissociations of the effects of amygdala and insular cortex lesions on conditioned taste aversion, passive avoidance, and neophobia in rat using the excitotoxin ibotenic acid. Behav Neurosci. 1988;102:3–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
