G alpha-q/11 protein plays a key role in insulin-induced glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- PMID: 10490615
- PMCID: PMC84673
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.6765
G alpha-q/11 protein plays a key role in insulin-induced glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Abstract
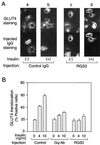
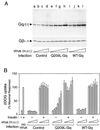
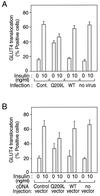
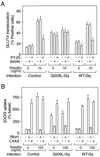
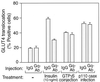
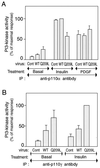
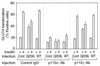
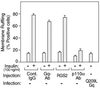
We evaluated the role of the G alpha-q (Galphaq) subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins in the insulin signaling pathway leading to GLUT4 translocation. We inhibited endogenous Galphaq function by single cell microinjection of anti-Galphaq/11 antibody or RGS2 protein (a GAP protein for Galphaq), followed by immunostaining to assess GLUT4 translocation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Galphaq/11 antibody and RGS2 inhibited insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation by 60 or 75%, respectively, indicating that activated Galphaq is important for insulin-induced glucose transport. We then assessed the effect of overexpressing wild-type Galphaq (WT-Galphaq) or a constitutively active Galphaq mutant (Q209L-Galphaq) by using an adenovirus expression vector. In the basal state, Q209L-Galphaq expression stimulated 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake and GLUT4 translocation to 70% of the maximal insulin effect. This effect of Q209L-Galphaq was inhibited by wortmannin, suggesting that it is phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) dependent. We further show that Q209L-Galphaq stimulates PI3-kinase activity in p110alpha and p110gamma immunoprecipitates by 3- and 8-fold, respectively, whereas insulin stimulates this activity mostly in p110alpha by 10-fold. Nevertheless, only microinjection of anti-p110alpha (and not p110gamma) antibody inhibited both insulin- and Q209L-Galphaq-induced GLUT4 translocation, suggesting that the metabolic effects induced by Q209L-Galphaq are dependent on the p110alpha subunit of PI3-kinase. In summary, (i) Galphaq appears to play a necessary role in insulin-stimulated glucose transport, (ii) Galphaq action in the insulin signaling pathway is upstream of and dependent upon PI3-kinase, and (iii) Galphaq can transmit signals from the insulin receptor to the p110alpha subunit of PI3-kinase, which leads to GLUT4 translocation.
Figures


References
-
- Araki E, Lipes M A, Patti M E, Brüning J C, Haag B, Johnson R S, Kahn C R. Alternative pathway of insulin signalling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene. Nature. 1994;372:186–190. - PubMed
-
- Chen D, Elmendorf J S, Olson A L, Li X, Earp H S. Osmotic shock stimulates GLUT4 translocation in 3T3L1 adipocytes by a novel tyrosine kinase pathway. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:27401–27410. - PubMed
-
- Clapham D E, Neer E J. G protein beta gamma subunits. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1997;37:167–203. - PubMed
-
- Daub H, Wallasch C, Ullrich A. Role of transactivation of the EGF receptor in signalling by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 1996;379:557–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
