The protein kinase Clk/Sty directly modulates SR protein activity: both hyper- and hypophosphorylation inhibit splicing
- PMID: 10490636
- PMCID: PMC84694
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.6991
The protein kinase Clk/Sty directly modulates SR protein activity: both hyper- and hypophosphorylation inhibit splicing
Abstract
The splicing of mammalian mRNA precursors requires both protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, likely involving modification of members of the SR protein family of splicing factors. Several kinases have been identified that can phosphorylate SR proteins in vitro, and transfection assays have provided evidence that at least one of these, Clk/Sty, can modulate splicing in vivo. But evidence that a specific kinase can directly affect the splicing activity of SR proteins has been lacking. Here, by using purified recombinant Clk/Sty, a catalytically inactive mutant, and individual SR proteins, we show that Clk/Sty directly affects the activity of SR proteins, but not other essential splicing factors, in reconstituted splicing assays. We also provide evidence that both hyper- and hypophosphorylation inhibit SR protein splicing activity, repressing constitutive splicing and switching alternative splice site selection. These findings indicate that Clk/Sty directly and specifically influences the activity of SR protein splicing factors and, importantly, show that both under- and overphosphorylation of SR proteins can modulate splicing.
Figures
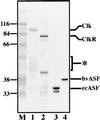
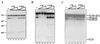



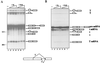
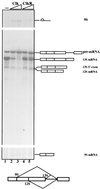
References
-
- Cáceres J F, Stamm S, Helfman D M, Krainer A R. Regulation of alternative splicing in vivo by overexpression of antagonistic splicing factors. Science. 1994;265:1706–1709. - PubMed
-
- Cardinali B, Cohen P, Lamond A I. Protein phosphatase PP1 can modulate 5′-splice site selection in a HeLa splicing extract. FEBS Lett. 1994;352:276–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
