zfh-1, the Drosophila homologue of ZEB, is a transcriptional repressor that regulates somatic myogenesis
- PMID: 10490660
- PMCID: PMC84718
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.7255
zfh-1, the Drosophila homologue of ZEB, is a transcriptional repressor that regulates somatic myogenesis
Abstract
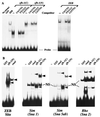
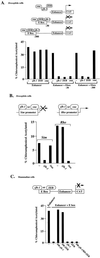
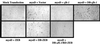
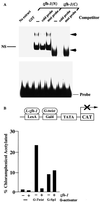
zfh-1 is a member of the zfh family of proteins, which all contain zinc finger and homeodomains. The roles and mechanisms of action of most family members are still unclear. However, we have shown previously that another member of the family, the vertebrate ZEB protein, is a transcriptional repressor that binds E box sequences and inhibits myotube formation in cell culture assays. zfh-1 is downregulated in Drosophila embryos prior to myogenesis. Embryos with zfh-1 loss-of-function mutation show alterations in the number and position of embryonic somatic muscles, suggesting that zfh-1 could have a regulatory role in myogenesis. However, nothing is known about the nature or mechanism of action of zfh-1. Here, we demonstrate that zfh-1 is a transcription factor that binds E box sequences and acts as an active transcriptional repressor. When zfh-1 expression was maintained in the embryo beyond its normal temporal pattern of downregulation, the differentiation of somatic but not visceral muscle was blocked. One potential target of zfh-1 in somatic myogenesis could be the myogenic factor mef2. mef2 is known to be regulated by the transcription factor twist, and we show here that zfh-1 binds to sites in the mef2 upstream regulatory region and inhibits twist transcriptional activation. Even though there is little sequence similarity in the repressor domains of ZEB and zfh-1, we present evidence that zfh-1 is the functional homologue of ZEB and that the role of these proteins in myogenesis is conserved from Drosophila to mammals.
Figures
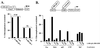

References
-
- Bate M. The mesoderm and its derivatives. In: Bate M, Martinez-Arias A, editors. The development of Drosophila melanoganster. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1993. pp. 1013–1090.
-
- Baylies M K, Bate M. Twist: a myogenic switch in Drosophila. Science. 1996;272:1481–1484. - PubMed
-
- Baylies M K, Bate M, Gomez M R. Myogenesis: a view from Drosophila. Cell. 1998;93:921–927. - PubMed
-
- Benezra R, Davis R L, Lockshon D, Turner D L, Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990;61:49–59. - PubMed
-
- Bour B A, O’Brien M A, Lockwood W L, Goldstein E S, Bodmer R, Taghert P H, Abmayr S M, Nguyen H T. Drosophila Mef2, a transcription factor that is essential for myogenesis. Genes Dev. 1995;15:730–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
