Regulation of p21(cip1) expression by growth factors and the extracellular matrix reveals a role for transient ERK activity in G1 phase
- PMID: 10491389
- PMCID: PMC2156121
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.146.6.1255
Regulation of p21(cip1) expression by growth factors and the extracellular matrix reveals a role for transient ERK activity in G1 phase
Abstract
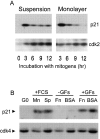
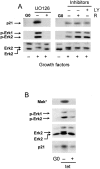
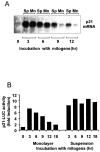
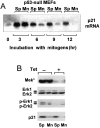
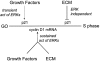
We have examined the regulation of p21(cip1) by soluble mitogens and cell anchorage as well as the relationship between the expression of p21(cip1) and activation of the ERK subfamily of MAP kinases. We find that p21(cip1) expression in G1 phase can be divided into two discrete phases: an initial induction that requires growth factors and the activation of ERK, and then a subsequent decline that is enhanced by cell anchorage in an ERK-independent manner. In contrast to the induction of cyclin D1, the induction of p21(cip1) is mediated by transient ERK activity. Comparative studies with wild-type and p21(cip1)-null fibroblasts indicate that adhesion-dependent regulation of p21(cip1) is important for proper control of cyclin E-cdk2 activity. These data lead to a model in which mitogens and anchorage act in a parallel fashion to regulate G1 phase expression of p21(cip1). They also show that (a) growth factors and growth factor/extracellular matrix cooperation can have different roles in regulating G1 phase ERK activity and (b) both transient and sustained ERK signals have functionally significant roles in controlling cell cycle progression through G1 phase.
Figures




References
-
- Albanese C., Johnson J., Watanabe G., Eklund N., Vu D., Arnold A., Pestell R.G. Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:23589–23597. - PubMed
-
- Aplin A.E., Juliano R.L. Integrin and cytoskeletal regulation of growth factor signaling to the MAP kinase pathway. J. Cell Sci. 1999;112:695–706. - PubMed
-
- Auer K.L., Park J.-S., Seth P., Coffey R.J., Darlingtons G., Abo A., McMahon M., DePinho R.A., Fisher P.B., Dent P. Prolonged activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway promotes DNA synthesis in primary hepatocytes from p21cip1/waf1-null mice, but not in hepatocytes from p16INK4a-null mice. Biochem. J. 1998;336:551–560. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

