Activity-dependent activation of TrkB neurotrophin receptors in the adult CNS
- PMID: 10492004
- PMCID: PMC311290
Activity-dependent activation of TrkB neurotrophin receptors in the adult CNS
Abstract
In this paper we have investigated the hypothesis that neural activity causes rapid activation of TrkB neurotrophin receptors in the adult mammalian CNS. These studies demonstrate that kainic acid-induced seizures led to a rapid and transient activation of TrkB receptors in the cortex. Subcellular fractionation demonstrated that these activated Trk receptors were preferentially enriched in the synaptosomal membrane fraction that also contained postsynaptic glutamate receptors. The fast activation of synaptic TrkB receptors could be duplicated in isolated cortical synaptosomes with KCl, presumably as a consequence of depolarization-induced BDNF release. Importantly, TrkB activation was also observed following pharmacological activation of brain-stem noradrenergic neurons, which synthesize and anterogradely transport BDNF; treatment with yohimbine led to activation of cortical TrkB receptors within 30 min. Pharmacological blockade of the postsynaptic alpha1-adrenergic receptors with prazosin only partially inhibited this effect, suggesting that the TrkB activation was partially due to a direct effect on postsynaptic cortical neurons. Together, these data support the hypothesis that activity causes release of BDNF from presynaptic terminals, resulting in a rapid activation of postsynaptic TrkB receptors. This activity-dependent TrkB activation could play a major role in morphological growth and remodelling in both the developing and mature nervous systems.
Figures
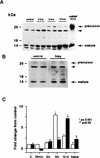







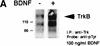
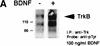
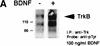
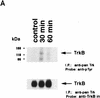



References
-
- Androutsellis-Theotokis A, McCormack WJ, Bradford HF, Stern GM, Pliego-Rivero FB. The depolarisation-induced release of [125I]BDNF from brain tissue. Brain Res. 1996;743:40–48. - PubMed
-
- Altar CA, Cai N, Bliven T, Juhasz M, Conner JM, Acheson AL, Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ. Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature. 1997;389:856–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
