Arachidonic acid reciprocally alters the availability of transient and sustained dendritic K(+) channels in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 10493718
- PMCID: PMC6783020
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-19-08163.1999
Arachidonic acid reciprocally alters the availability of transient and sustained dendritic K(+) channels in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
Abstract
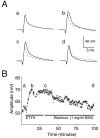
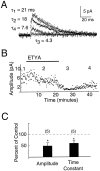
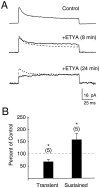
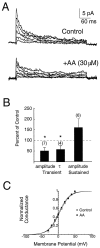
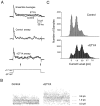
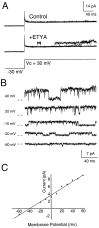
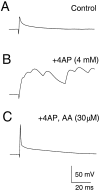
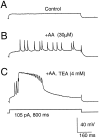
The dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell dendrites express a high density of transient A-type K(+) channels, which play a critical role in the back-propagation of action potentials and in the determination of dendritic excitability. Recently, arachidonic acid and its nonmetabolizable analogue 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA) were shown to block transient K(+) channels in the somata of these cells (), but to have little effect on the somatic action potential. In the present study we have investigated the effects of arachidonic acid and ETYA on the gating of channels and the excitability of the apical dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. We found not only a block of transient K(+) channels, but also an enhancement of sustained outward currents. The sustained currents consisted of at least two distinct channel types. The larger conductance channel (>50 pS) was identified as a K(+) channel. Arachidonic acid greatly enhanced the amplitude of back-propagating dendritic action potentials (>200 micrometer from the soma) but did not result in sustained depolarizations of the dendrites similar to those seen with 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) application. In fact, arachidonic acid reduced dendritic excitability when applied after 4-AP. Thus, arachidonic acid appears to cause a shift of available channels from the fast, transient type to the slower, sustained types. The net effect appears to be an enhancement of dendritic action potential amplitude that occurs without compromising the electrical stability of the dendrites.
Figures


References
-
- Breukel AI, Besselsen E, Lopes da Silva FH, Lopes da Silva FH, Ghijsen WE. Arachidonic acid inhibits uptake of amino acids and potentiates PKC effects on glutamate, but not GABA, exocytosis in isolated hippocampal nerve terminals. Brain Res. 1997;773:90–97. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G, Kandel A. Somadendritic backpropagation of action potentials in cortical pyramidal cells of the awake rat. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:1587–1591. - PubMed
-
- Callaway JC, Ross WN. Frequency-dependent propagation of sodium action potentials in dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1995;74:1395–1403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
