Characterization of an NGF-P-TrkA retrograde-signaling complex and age-dependent regulation of TrkA phosphorylation in sympathetic neurons
- PMID: 10493722
- PMCID: PMC6783056
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-19-08207.1999
Characterization of an NGF-P-TrkA retrograde-signaling complex and age-dependent regulation of TrkA phosphorylation in sympathetic neurons
Abstract
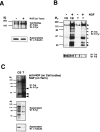
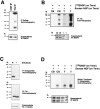
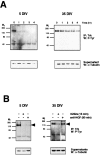
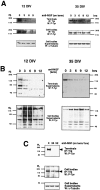
Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a target-derived trophic factor for developing sympathetic and cutaneous sensory neurons. NGF promotes growth and survival of neurons via activation of the receptor tyrosine kinase TrkA. We used compartmentalized cultures of sympathetic neurons to address the mechanism of NGF signaling from distal axons and terminals to proximal axons and cell bodies. Our results demonstrate that an NGF-phospho-TrkA (NGF-P-TrkA)-signaling complex forms in distal axons and is retrogradely transported as a complex to cell bodies of sympathetic neurons. Although a minor fraction of both NGF and TrkA is retrogradely transported, a large fraction of the NGF that is retrogradely transported is found complexed with retrogradely transported TrkA. Interestingly, the metabolism of the P-TrkA complex is dramatically different in young, NGF-dependent sympathetic neurons as compared to older, NGF-independent sympathetic neurons. After withdrawal of NGF from distal axons of young neurons, P-TrkA within distal axons, as well as within proximal axons and cell bodies, dephosphorylates rapidly. In contrast, after withdrawal of NGF from distal axons of older neurons, P-TrkA within distal axons dephosphorylates completely, although more slowly than that in young neurons, whereas dephosphorylation of P-TrkA within proximal axons and cell bodies occurs markedly more slowly, with at least one-half of the level of P-TrkA remaining 2 d after NGF withdrawal. Thus, P-TrkA within the cell bodies of young, NGF-dependent sympathetic neurons is derived from distal axons. A more stable P-TrkA complex within cell bodies of mature sympathetic neurons may contribute to the acquisition of NGF independence for survival of mature sympathetic neurons.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid retrograde tyrosine phosphorylation of trkA and other proteins in rat sympathetic neurons in compartmented cultures.J Cell Biol. 1997 Jul 28;138(2):411-21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.2.411. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9230082 Free PMC article.
-
A nerve growth factor-induced retrograde survival signal mediated by mechanisms downstream of TrkA.Neuropharmacology. 2007 Feb;52(2):270-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.07.032. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Neuropharmacology. 2007. PMID: 16949623
-
An NGF-TrkA-mediated retrograde signal to transcription factor CREB in sympathetic neurons.Science. 1997 Aug 22;277(5329):1097-100. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5329.1097. Science. 1997. PMID: 9262478
-
Neurotrophin receptors: mediators of life and death.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998 May;26(2-3):295-301. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(97)00036-2. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998. PMID: 9651545 Review.
-
Functional roles of neurotrophin 3 in the developing and mature sympathetic nervous system.Mol Neurobiol. 1996 Dec;13(3):185-97. doi: 10.1007/BF02740622. Mol Neurobiol. 1996. PMID: 8989769 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro and in vivo study of effects of fermented soybean product (chungkookjang) on NGF secretion ability and NGF receptor signaling pathway.Lab Anim Res. 2013 Jun;29(2):113-26. doi: 10.5625/lar.2013.29.2.113. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Lab Anim Res. 2013. PMID: 23825484 Free PMC article.
-
Axon myelination and electrical stimulation in a microfluidic, compartmentalized cell culture platform.Neuromolecular Med. 2012 Jun;14(2):112-8. doi: 10.1007/s12017-012-8170-5. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Neuromolecular Med. 2012. PMID: 22527791
-
CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) enhances casitas B lineage lymphoma-3/c (Cbl-3/c)-mediated Ret isoform-specific ubiquitination and degradation via its amino-terminal Src homology 3 domains.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 14;289(11):7307-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.537878. Epub 2014 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24425877 Free PMC article.
-
APPL1 associates with TrkA and GIPC1 and is required for nerve growth factor-mediated signal transduction.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(23):8928-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00228-06. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17000777 Free PMC article.
-
Production of compartmented cultures of rat sympathetic neurons.Nat Protoc. 2009;4(12):1869-87. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.210. Nat Protoc. 2009. PMID: 20010935
References
-
- Angeletti PU, Levi-Montalcini R, Caramia F. Analysis of the effects of the antiserum to the nerve growth factor in adult mice. Brain Res. 1971;27:343–355. - PubMed
-
- Barde Y-A. Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron. 1989;2:1525–1534. - PubMed
-
- Berg MM, Sternberg DW, Parada LF, Chao MV. K-252a inhibits nerve growth factor-induced trk proto-oncogene tyrosine phosphorylation and kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13–16. - PubMed
-
- Bjette B, Wilkund L, Edwards DC. A study of the de- and regenerative changes in the sympathetic nervous system of the adult mouse after treatment with antisera to NGF. Brain Res. 1975;92:257–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
