Both the neuronal and inducible isoforms contribute to upregulation of retinal nitric oxide synthase activity by brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PMID: 10493752
- PMCID: PMC6783014
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-19-08517.1999
Both the neuronal and inducible isoforms contribute to upregulation of retinal nitric oxide synthase activity by brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Abstract
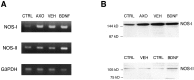
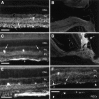
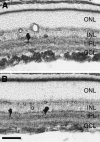
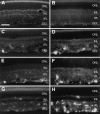
Although neurotrophins are best known for their trophic functions, growing evidence suggests that neurotrophins can also be neurotoxic, for instance by enhancing excitotoxic insults. We have shown recently that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) limits its neuroprotective action on axotomized rat retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) by upregulating nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity (Klöcker et al., 1998). The aim of the present study was to investigate this interaction of BDNF and NOS in the lesioned adult rat retina in more detail. We used NOS immunohistochemistry and NADPH-diaphorase (NADPH-d) reaction to characterize morphologically retinal NOS expression and activity. Using reverse transcription-PCR and Western blot analysis, we were able to identify the NOS isoforms being regulated. Six days after optic nerve lesion, we observed an increase in neuronal NOS (NOS-I) mRNA and protein expression in the inner retina. This did not lead to a marked increase in overall retinal NOS activity. Only RGC axons displayed strong de novo NADPH-d reactivity. In contrast, intraocular injection of BDNF resulted in a marked upregulation of NOS activity in NOS-I-immunoreactive structures, leaving the level of NOS-I expression unchanged. In addition, an induction of inducible NOS (NOS-II) was found after BDNF treatment. We identified microglial cells increasing in number and being activated by BDNF, which could serve as the cellular source of NOS-II. In summary, our data suggest that BDNF upregulates retinal NOS activity by both a post-translational regulation of NOS-I activity and an induction of NOS-II. These findings might be useful for developing pharmacological strategies to improve BDNF-mediated neuroprotection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on the development of NADPH-diaphorase/nitric oxide synthase-positive amacrine cells in the rodent retina.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Aug;11(8):2824-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00690.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10457179
-
Free radical scavenging and inhibition of nitric oxide synthase potentiates the neurotrophic effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on axotomized retinal ganglion cells In vivo.J Neurosci. 1998 Feb 1;18(3):1038-46. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-03-01038.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9437024 Free PMC article.
-
CNTF and BDNF have similar effects on retinal ganglion cell survival but differential effects on nitric oxide synthase expression soon after optic nerve injury.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Apr;46(4):1497-503. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0664. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15790921
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase immunoreactive neurons in the mammalian retina.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Jul 15;50(2):112-23. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20000715)50:2<112::AID-JEMT3>3.0.CO;2-S. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10891875 Review.
-
A molecular mechanism of optic nerve regeneration in fish: the retinoid signaling pathway.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013 Nov;37:13-30. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23994437 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuregulin signaling via erbB receptor assemblies in the nervous system.Mol Neurobiol. 2002 Feb;25(1):67-77. doi: 10.1385/MN:25:1:067. Mol Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 11890458 Review.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated neuroprotection of adult rat retinal ganglion cells in vivo does not exclusively depend on phosphatidyl-inositol-3'-kinase/protein kinase B signaling.J Neurosci. 2000 Sep 15;20(18):6962-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-18-06962.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10995840 Free PMC article.
-
The role of nitric oxide in the apoptosis of neurons in the retina of the human fetal eye.Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2007 Feb;37(2):111-8. doi: 10.1007/s11055-007-0157-6. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17187201
-
Reduction of potassium currents and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent AKT phosphorylation by tumor necrosis factor-(alpha) rescues axotomized retinal ganglion cells from retrograde cell death in vivo.J Neurosci. 2001 Mar 15;21(6):2058-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-06-02058.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11245689 Free PMC article.
-
Role of BDNF/TrkB pathway in the visual system: Therapeutic implications for glaucoma.Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2017;12(1):69-81. doi: 10.1080/17469899.2017.1259566. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28751923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley; New York: 1987.
-
- Barbacid M. Neurotrophic factors and their receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995;7:148–155. - PubMed
-
- Block F, Schwarz M. Memantine reduces functional and morphological consequences induced by global ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1996;208:41–44. - PubMed
-
- Brandstatter JH, Hartveit E, Sassoe Pognetto M, Wassle H. Expression of NMDA and high-affinity kainate receptor subunit mRNAs in the adult rat retina. Eur J Neurosci. 1994;6:1100–1112. - PubMed
-
- Brenman JE, Bredt DS. Synaptic signaling by nitric oxide. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1997;7:374–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
