Modulation of cytokine response of pneumonic foals by virulent Rhodococcus equi
- PMID: 10496876
- PMCID: PMC96851
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.10.5041-5047.1999
Modulation of cytokine response of pneumonic foals by virulent Rhodococcus equi
Abstract
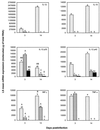
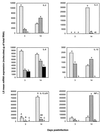
The ability of Rhodococcus equi to induce pneumonia in foals depends on the presence of an 85- to 90-kb plasmid. In this study, we evaluated whether plasmid-encoded products mediate virulence by modulating the cytokine response of foals. Foals infected intrabronchially with a virulence plasmid-containing strain of R. equi had similar gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and interleukin-12 (IL-12) p35 but significantly higher IL-1beta, IL-10, IL-12 p40, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) mRNA expression in lung tissue compared to foals infected with the plasmid-cured derivative. IFN-gamma mRNA expression levels in CD4+ T lymphocytes isolated from bronchial lymph nodes (BLN) were similar for the two groups of R. equi-infected foals on day 3 postinfection. However, on day 14, in association with pneumonia and marked multiplication of virulent R. equi but with complete clearance of the plasmid-cured derivative, IFN-gamma mRNA expression in BLN CD4+ T lymphocytes was significantly (P < 0.001) higher in foals infected with the plasmid-cured derivative. These results suggests an immunomodulating role for R. equi virulence plasmid-encoded products in downregulating IFN-gamma mRNA expression by CD4+ T lymphocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental infection of neonatal foals with Rhodococcus equi triggers adult-like gamma interferon induction.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Jun;14(6):669-77. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00042-07. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17409222 Free PMC article.
-
Clearance of virulent but not avirulent Rhodococcus equi from the lungs of adult horses is associated with intracytoplasmic gamma interferon production by CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003 Mar;10(2):208-15. doi: 10.1128/cdli.10.2.208-215.2003. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12626444 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo expression of and cell-mediated immune responses to the plasmid-encoded virulence-associated proteins of Rhodococcus equi in foals.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Apr;14(4):369-74. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00448-06. Epub 2007 Feb 14. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17301216 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodococcus equi: clinical manifestations, virulence, and immunity.J Vet Intern Med. 2011 Nov-Dec;25(6):1221-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.2011.00804.x. Epub 2011 Oct 7. J Vet Intern Med. 2011. PMID: 22092609 Review.
-
Pathogenesis and virulence of Rhodococcus equi.Vet Microbiol. 1997 Jun 16;56(3-4):257-68. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(97)00094-1. Vet Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9226840 Review.
Cited by
-
Streptolysin-O/antibiotics adjunct therapy modulates site-specific expression of extracellular matrix and inflammatory genes in lungs of Rhodococcus equi infected foals.Vet Res Commun. 2013 Jun;37(2):145-54. doi: 10.1007/s11259-013-9557-y. Epub 2013 Mar 9. Vet Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23475766
-
Rhodococcus equi-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promoting Inflammatory Response in Macrophage through TLR2-NF-κB/MAPK Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 28;23(17):9742. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179742. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077142 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin G subisotype responses of pneumonic and healthy, exposed foals and adult horses to Rhodococcus equi virulence-associated proteins.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003 May;10(3):345-51. doi: 10.1128/cdli.10.3.345-351.2003. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12738629 Free PMC article.
-
PNAG-specific equine IgG1 mediates significantly greater opsonization and killing of Prescottella equi (formerly Rhodococcus equi) than does IgG4/7.Vaccine. 2019 Feb 21;37(9):1142-1150. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.01.028. Epub 2019 Jan 26. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 30691984 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental infection of neonatal foals with Rhodococcus equi triggers adult-like gamma interferon induction.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Jun;14(6):669-77. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00042-07. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17409222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arlotti M, Boboli G, Moscatelli G L, Magnati G, Maserati R, Borghi V, Andreoni M, Libanore M, Bonazzi L, Piscina A, Ciammarughi R. Rhodococcus equi infection in HIV-positive subjects: a retrospective analysis of 24 cases. Scand J Infect Dis. 1996;28:463–467. - PubMed
-
- Balson G A, Smith G D, Yager J A. Immunophenotypic analysis of foal bronchoalveolar lymphocytes. Vet Microbiol. 1997;56:237–246. - PubMed
-
- Balson G A, Yager J A, Croy B A. SCID/beige mice in the study of immunity to Rhodococcus equi. In: Rossdale P D, Wade J F, editors. Equine infectious diseases. 6th ed. New Market, United Kingdom: R&W Publications; 1992. pp. 49–53.
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
-
- de la Pena-Moctezuma A, Prescott J F. Association with HeLa cells by Rhodococcus equi with and without the virulence plasmid. Vet Microbiol. 1995;46:383–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

