Humoral and cellular immune responses in mice immunized with recombinant Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin producing a pertussis toxin-tetanus toxin hybrid protein
- PMID: 10496883
- PMCID: PMC96858
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.10.5100-5105.1999
Humoral and cellular immune responses in mice immunized with recombinant Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin producing a pertussis toxin-tetanus toxin hybrid protein
Abstract
The development of combined vaccines constitutes one of the priorities in modern vaccine research. One of the most successful combined vaccines in use is the diphtheria-pertussis-tetanus vaccine. However, concerns about the safety of the pertussis arm have led to decreased acceptance of the vaccine but also to the development of new, safer, and effective acellular vaccines against pertussis. Unfortunately, the production cost of these new vaccines is significantly higher than that of previous vaccines. Here, we explore the potential of live recombinant Mycobacterium bovis BCG producing the hybrid protein S1-TTC, which contains the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin fused to fragment C of tetanus toxin, as an alternative to the acellular vaccines. S1-TTC was produced in two different expression systems. In the first system its production was under the control of the 85A antigen promoter and signal peptide, and in the second system it was under the control of the hsp60 promoter. Although expression of the hybrid antigen was obtained in both cases, only the second expression system yielded a recombinant BCG strain able to induce both a specific humoral immune response and a specific cellular immune response. The antibodies generated were directed against the TTC part and neutralized toxin activity in an in vivo challenge model, whereas interleukin-2 production was specific for both parts of the molecule. Since protection against tetanus is antibody mediated and protection against pertussis may be cell mediated, this constitutes a first promising step towards the development of a cost-effective, protective, and safe combined vaccine against pertussis, tetanus, and tuberculosis.
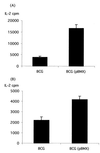
Figures


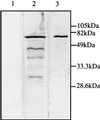
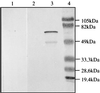
References
-
- Abomoelak, B., et al. Unpublished data.
-
- Ad Hoc Group for the Study of Pertussis Vaccines. Placebo-controlled trial of two acellular pertussis vaccines in Sweden—protective efficacy and adverse events. Lancet. 1988;i:955–960. . (Erratum, Lancet i:1238). - PubMed
-
- Aldovini A, Young R A. Humoral and cell-mediated immune responses to live recombinant BCG-HIV vaccines. Nature. 1991;351:479–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

