Fasciola hepatica suppresses a protective Th1 response against Bordetella pertussis
- PMID: 10496919
- PMCID: PMC96894
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.10.5372-5378.1999
Fasciola hepatica suppresses a protective Th1 response against Bordetella pertussis
Abstract
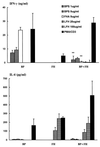
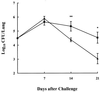
Fasciolosis, like other helminth infections, is associated with the induction of T-cell responses polarized to the Th2 subtype. Respiratory infection with Bordetella pertussis or immunization with a pertussis whole-cell vaccine (Pw) induces a potent Th1 response, which confers a high level of protection against bacterial challenge. We have used these two pathogens to examine bystander cross-regulation of Th1 and Th2 cells in vivo and provide evidence of immunomodulation of host T-cell responses to B. pertussis by a concomitant infection with Fasciola hepatica. Mice with a coinfection of F. hepatica and B. pertussis exhibited a Th2 cytokine profile in response to F. hepatica antigens, similar to those infected with F. hepatica alone. By contrast, the Th1 response to B. pertussis antigens was markedly suppressed and the bacterial infection was exacerbated following infection with F. hepatica. Furthermore, an established Th1 response induced in mice by infection with B. pertussis or by parenteral immunization with Pw was also suppressed following infection with F. hepatica. This immunomodulatory effect of B. pertussis-induced responses by F. hepatica infection is significantly reduced, but not completely abrogated, in IL-4 knockout mice. Our findings demonstrate that Th2-inducing parasites can exert bystander suppression of protective Th1 responses to infection or vaccination with a bacterial pathogen and that the modulation is mediated in part by IL-4 and, significantly, is effective at both the induction and effector stages of the Th1 response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Th1/Th2 cell dichotomy in acquired immunity to Bordetella pertussis: variables in the in vivo priming and in vitro cytokine detection techniques affect the classification of T-cell subsets as Th1, Th2 or Th0.Immunology. 1996 Mar;87(3):372-80. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1996.497560.x. Immunology. 1996. PMID: 8778021 Free PMC article.
-
Fasciola hepatica cathepsin L cysteine proteinase suppresses Bordetella pertussis-specific interferon-gamma production in vivo.Parasite Immunol. 2001 Oct;23(10):541-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3024.2001.00411.x. Parasite Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11696165
-
A regulatory role for interleukin 4 in differential inflammatory responses in the lung following infection of mice primed with Th1- or Th2-inducing pertussis vaccines.Infect Immun. 2000 Mar;68(3):1383-90. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.3.1383-1390.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10678951 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity to the respiratory pathogen Bordetella pertussis.Mucosal Immunol. 2012 Sep;5(5):485-500. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.54. Epub 2012 Jun 20. Mucosal Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22718262 Review.
-
Distinct immunological states in murine cutaneous leishmaniasis by immunising with different amounts of antigen: the generation of beneficial, potentially harmful, harmful and potentially extremely harmful states.Behring Inst Mitt. 1997 Feb;(98):153-9. Behring Inst Mitt. 1997. PMID: 9382736 Review.
Cited by
-
Somatic antigens of tropical liver flukes ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis in wistar rats.PLoS One. 2015 May 18;10(5):e0126429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126429. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992888 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Fasciola hepatica infection alters responses to tests used for diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 2007 Mar;75(3):1373-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01445-06. Epub 2006 Dec 28. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17194810 Free PMC article.
-
How pathogen-derived cysteine proteases modulate host immune responses.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;712:192-207. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-8414-2_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21660666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pertussis: Microbiology, Disease, Treatment, and Prevention.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Jul;29(3):449-86. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00083-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27029594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fasciola hepatica infection reduces Mycobacterium bovis burden and mycobacterial uptake and suppresses the pro-inflammatory response.Parasite Immunol. 2016 Jul;38(7):387-402. doi: 10.1111/pim.12326. Parasite Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27108767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas A K, Murphy K M, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Allen J E, MacDonald A S. Profound suppression of cellular proliferation mediated by the secretions of nematodes. Parasite Immunol. 1998;20:241–247. - PubMed
-
- Bohn E, Sing A, Zumbihl R, Bielfeldt C, Okamura H, Kurimoto M, Heesemann J, Autenriech I B. IL-18 (IFN-γ inducing factor) regulates early cytokine production, and promotes the resolution of bacterial infection in mice. J Immunol. 1998;160:299–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

