Infection of endothelial cells with Trypanosoma cruzi activates NF-kappaB and induces vascular adhesion molecule expression
- PMID: 10496926
- PMCID: PMC96901
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.10.5434-5440.1999
Infection of endothelial cells with Trypanosoma cruzi activates NF-kappaB and induces vascular adhesion molecule expression
Abstract
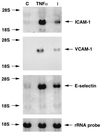
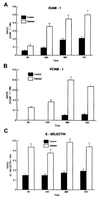
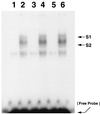
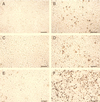
Transcriptional activation of vascular adhesion molecule expression, a major component of an inflammatory response, is regulated, in part, by the nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel (NF-kappaB) family of transcription factors. We therefore determined whether Trypanosoma cruzi infection of endothelial cells resulted in the activation of NF-kappaB and the induction or increased expression of adhesion molecules. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were infected with trypomastigotes of the Tulahuen strain of T. cruzi. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays with an NF-kappaB-specific oligonucleotide and nuclear extracts from T. cruzi-infected HUVEC (6 to 48 h postinfection) detected two major shifted complexes. Pretreatment with 50x cold NF-kappaB consensus sequence abolished both gel-shifted complexes while excess SP-1 consensus sequence had no effect. These data indicate that nuclear extracts from T. cruzi-infected HUVEC specifically bound to the NF-kappaB consensus DNA sequence. Supershift analysis revealed that the gel-shifted complexes were comprised of p65 (RelA) and p50 (NF-kappaB1). Northern blot analyses demonstrated both the induction of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 and E-selectin and the upregulation of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 mRNA in HUVEC infected with T. cruzi. Immunocytochemical staining confirmed adhesion molecule expression in response to T. cruzi infection. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that the activation of the NF-kappaB pathway in endothelial cells associated with T. cruzi infection may be an important factor in the inflammatory response and subsequent vascular injury and endothelial dysfunction that lead to chronic cardiomyopathy.
Figures

References
-
- Carlos T, Kovach N, Schwartz B, Rosa M, Newman B, Wayner E, Benjamin C, Osborn L, Lobb R, Harlan J. Human monocytes bind to two cytokine-induced adhesive ligands on cultured human endothelial cells: endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Blood. 1991;77:2266–2271. - PubMed
-
- Collins T. Endothelial nuclear factor-κB and the initiation of the arteriosclerotic lesion. Lab Investig. 1993;68:499–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

