Growth rate of mycobacteria in mice as an unreliable indicator of mycobacterial virulence
- PMID: 10496935
- PMCID: PMC96910
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.10.5483-5485.1999
Growth rate of mycobacteria in mice as an unreliable indicator of mycobacterial virulence
Abstract
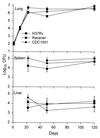
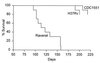
The CDC1551 strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis was compared with the H37Rv strain of M. tuberculosis and the Ravenel strain of Mycobacterium bovis for virulence in mice. Although all three strains gave rise to the same level of stationary infection in major organs, mice infected with the Ravenel strain died much earlier from lung disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virulence ranking of some Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis strains according to their ability to multiply in the lungs, induce lung pathology, and cause mortality in mice.Infect Immun. 1995 Sep;63(9):3428-37. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.9.3428-3437.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7642273 Free PMC article.
-
An attempt to cultivate mycobacteria in simple synthetic liquid medium containing lecithin-cholesterol liposomes.Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1976 Jun;29(3):109-21. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.29.109. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1976. PMID: 824481
-
Mycobacterial virulence. Virulent strains of Mycobacteria tuberculosis have faster in vivo doubling times and are better equipped to resist growth-inhibiting functions of macrophages in the presence and absence of specific immunity.J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1723-33. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1723. J Exp Med. 1993. PMID: 8496688 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterial manipulation of the host cell.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005 Nov;29(5):1041-50. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2005.04.013. Epub 2005 Jul 1. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16040149 Review.
-
Relationships between the structure and the roles of lipoarabinomannans and related glycoconjugates in tuberculosis pathogenesis.Front Biosci. 1998 Aug 6;3:e149-63. doi: 10.2741/a372. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9696885 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome Sequences of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Biovar bovis Strains Ravenel and 10-7428.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2021 Jun 17;10(24):e0041121. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00411-21. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2021. PMID: 34137637 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of Rv2525c, a substrate of the twin arginine translocation (Tat) system of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, increases beta-lactam susceptibility and virulence.J Bacteriol. 2006 Sep;188(18):6669-79. doi: 10.1128/JB.00631-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16952959 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term protection against tuberculosis following vaccination with a severely attenuated double lysine and pantothenate auxotroph of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 2005 Feb;73(2):1196-203. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.2.1196-1203.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15664964 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium bovis BCG immunization induces protective immunity against nine different Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains in mice.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):5173-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00019-08. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18710860 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis MmpL protein family to virulence and drug resistance.Infect Immun. 2005 Jun;73(6):3492-501. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3492-3501.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15908378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsaadi A-I, Smith D W. The fate of virulent and attenuated mycobacteria in guinea pigs infected by the respiratory route. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975;107:1041–1046. - PubMed
-
- Barnes P, Block A B, Davidson P T, Snider D E. Tuberculosis in patients with immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1644–1650. - PubMed
-
- Farer L S. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis in the United States. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;109:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Hill R A, Pemkuma S, Brustein S, Vaidya K, Powell S, Li P-W, Suster B. Disseminated tuberculosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome era. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;144:1164–1170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

