Expression of the Staphylococcus aureus UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl- L-alanyl-D-glutamate:L-lysine ligase in Escherichia coli and effects on peptidoglycan biosynthesis and cell growth
- PMID: 10498701
- PMCID: PMC103616
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.19.5909-5914.1999
Expression of the Staphylococcus aureus UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl- L-alanyl-D-glutamate:L-lysine ligase in Escherichia coli and effects on peptidoglycan biosynthesis and cell growth
Abstract
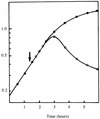
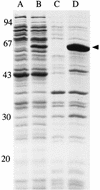
The monomer units in the Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus cell wall peptidoglycans differ in the nature of the third amino acid in the L-alanyl-gamma-D-glutamyl-X-D-alanyl-D-alanine side chain, where X is meso-diaminopimelic acid or L-lysine, respectively. The murE gene from S. aureus encoding the UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate: L-lysine ligase was identified and cloned into plasmid vectors. Induction of its overexpression in E. coli rapidly results in abnormal morphological changes and subsequent cell lysis. A reduction of 28% in the peptidoglycan content was observed in induced cells, and analysis of the peptidoglycan composition and structure showed that ca. 50% of the meso-diaminopimelic acid residues were replaced by L-lysine. Lysine was detected in both monomer and dimer fragments, but the acceptor units from the latter contained exclusively meso-diaminopimelic acid, suggesting that no transpeptidation could occur between the epsilon-amino group of L-lysine and the alpha-carboxyl group of D-alanine. The overall cross-linking of the macromolecule was only slightly decreased. Detection and analysis of meso-diaminopimelic acid- and L-lysine-containing peptidoglycan precursors confirmed the presence of L-lysine in precursors containing amino acids added after the reaction catalyzed by the MurE ligase and provided additional information about the specificity of the enzymes involved in these latter processes.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson M S, Eveland S S, Onishi H R, Pompliano D L. Kinetic mechanism of the Escherichia coli UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide d-alanyl-d-alanine-adding enzyme: use of a glutathione S-transferase fusion. Biochemistry. 1996;35:16264–16269. - PubMed
-
- Auger A, Martin L, Bertrand J, Ferrari P, Fanchon E, Vaganay S, Pétillot Y, van Heijenoort J, Blanot D, Dideberg O. Large-scale preparation, purification, and cristallization of UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine:d-glutamate ligase from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 1998;13:23–29. - PubMed
-
- Auger G, van Heijenoort J, Vederas J C, Blanot D. Effect of analogs of diaminopimelic acid on the meso-diaminopimelate-adding enzyme from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1996;391:171–174. - PubMed
-
- Braun V, Rehn K. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969;10:426–438. - PubMed
-
- Bugg T D H, Dutka-Malen S, Arthur M, Courvalin P, Walsh C T. Identification of vancomycin resistance protein VanA as a d-alanine:d-alanine ligase of altered substrate specificity. Biochemistry. 1991;30:2017–2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

