Identification of a regulator that controls stationary-phase expression of catalase-peroxidase in Caulobacter crescentus
- PMID: 10498730
- PMCID: PMC103645
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.19.6152-6159.1999
Identification of a regulator that controls stationary-phase expression of catalase-peroxidase in Caulobacter crescentus
Abstract
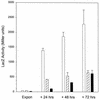
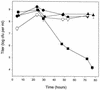
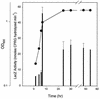
Expression of the catalase-peroxidase of Caulobacter crescentus, a gram-negative member of the alpha subdivision of the Proteobacteria, is 50-fold higher in stationary-phase cultures than in exponential cultures. To identify regulators of the starvation response, Tn5 insertion mutants were isolated with reduced expression of a katG::lacZ fusion on glucose starvation. One insertion interrupted an open reading frame encoding a protein with significant amino acid sequence identity to TipA, a helix-turn-helix transcriptional activator in the response of Streptomyces lividans to the peptide antibiotic thiostrepton, and lesser sequence similarity to other helix-turn-helix regulators in the MerR family. The C. crescentus orthologue of tipA was named skgA (stationary-phase regulation of katG). Stationary-phase expression of katG was reduced by 70% in the skgA::Tn5 mutant, and stationary-phase resistance to hydrogen peroxide decreased by a factor of 10. Like the wild type, the skgA mutant exhibited starvation-induced cross-resistance to heat and acid shock, entered into the helical morphology that occurs after 9 to 12 days in stationary phase, and during exponential growth induced katG in response to hydrogen peroxide challenge. Expression of skgA increased 5- to 10-fold in late exponential phase. skgA is the first regulator of a starvation-induced stress response identified in C. crescentus. SkgA is not a global regulator of the stationary-phase stress response; its action encompasses the oxidative stress-hydrogen peroxide response but not acid or heat responses. Moreover, SkgA is not an alternative sigma factor, like RpoS, which controls multiple aspects of starvation-induced cross-resistance to stress in enteric bacteria. These observations raise the possibility that regulation of stationary-phase gene expression in this member of the alpha subdivision of the Proteobacteria is different from that in Escherichia coli and other members of the gamma subdivision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Catalase-peroxidase of Caulobacter crescentus: function and role in stationary-phase survival.J Bacteriol. 1997 Nov;179(21):6831-6. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.21.6831-6836.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9352936 Free PMC article.
-
Catalase-peroxidase activity is decreased in a Caulobacter crescentus rho mutant.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010 Feb;303(1):48-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01860.x. Epub 2009 Nov 23. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20002190
-
Regulation of catalase-peroxidase KatG is OxyR dependent and Fur independent in Caulobacter crescentus.J Bacteriol. 2011 Apr;193(7):1734-44. doi: 10.1128/JB.01339-10. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21257767 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hydroperoxidase (catalase) expression in Escherichia coli.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995 Sep 1;131(2):113-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07764.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995. PMID: 7557318 Review.
-
Bacterial lifestyle shapes stringent response activation.Trends Microbiol. 2013 Apr;21(4):174-80. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Trends Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23419217 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for antibiotic recognition by the TipA class of multidrug-resistance transcriptional regulators.EMBO J. 2003 Apr 15;22(8):1824-34. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg181. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12682015 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of the stationary phase response regulator SpdR in Caulobacter crescentus.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Apr 12;16:66. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0682-y. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27072651 Free PMC article.
-
A caulobacter crescentus extracytoplasmic function sigma factor mediating the response to oxidative stress in stationary phase.J Bacteriol. 2006 Mar;188(5):1835-46. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.5.1835-1846.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16484194 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic binding releases autoinhibition of the TipA multidrug-resistance transcriptional regulator.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 18;295(51):17865-17876. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.016295. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33454020 Free PMC article.
-
PhyR is involved in the general stress response of Methylobacterium extorquens AM1.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(3):1027-35. doi: 10.1128/JB.01483-07. Epub 2007 Nov 16. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18024517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984;108:121–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

