Development of CD8alpha/alpha and CD8alpha/beta T cells in major histocompatibility complex class I-deficient mice
- PMID: 10499926
- PMCID: PMC2195628
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.190.6.881
Development of CD8alpha/alpha and CD8alpha/beta T cells in major histocompatibility complex class I-deficient mice
Abstract
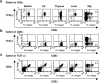
Peripheral CD8(+) T cells mainly use CD8alpha/beta, and their development is mainly dependent on the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I proteins K(b) and D(b) in H-2(b) mice. In this report, we have shown that the development of CD8alpha/beta TCR-alpha/beta cells in lymphoid organs as well as in intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (iIELs) is dependent on the MHC class I K(b) and D(b) proteins. In contrast, TCR-alpha/beta CD8alpha/alpha cells are found mainly in iIELs, and their numbers are unaffected in K(b)D(b) double knockout mice. Most of the TCR-gamma/delta cells in the iIELs also bear CD8alpha/alpha, and they are also unaffected in K(b)D(b) -/- mice. In beta2-microglobulin (beta2m)-deficient mice, all of the TCR-alpha/beta CD8alpha/alpha and CD8alpha/beta T cells disappear, but TCR-gamma/delta cells are unaffected by the absence of beta2m.
Figures
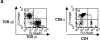
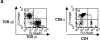



References
-
- Zijlstra M., Bix M., Semister N.E., Loring J.M., Raulet D.H., Jaenisch R. β2-microglobulin deficient mice lack CD4−CD8+ cytolytic T cells. Nature. 1990;344:742–746. - PubMed
-
- Raulet D.H. MHC class I-deficient mice. Adv. Immunol. 1994;55:381–421. - PubMed
-
- Van Kaer L., Ashton-Rickard P.G., Ploegh H.L., Tonegawa S. TAP1 mutant mice are deficient in antigen presentation, surface class I molecules and CD4−CD8+ T cells. Cell. 1992;71:1205–1214. - PubMed
-
- Lefrancois L. Phenotypic complexity of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. J. Immunol. 1991;147:1746–1751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

