Soluble member(s) of the mesothelin/megakaryocyte potentiating factor family are detectable in sera from patients with ovarian carcinoma
- PMID: 10500211
- PMCID: PMC18068
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11531
Soluble member(s) of the mesothelin/megakaryocyte potentiating factor family are detectable in sera from patients with ovarian carcinoma
Abstract
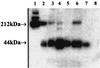
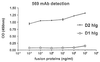
mAb OV569 was made by immunizing mice with ovarian carcinoma cells. It binds to cells from ovarian carcinomas and, to a lesser extent, to cells from certain other carcinomas whereas the binding to normal tissues is low to nondetectable. It also binds to soluble molecule(s) in culture supernatants from antigen-positive carcinomas. OV569 recognizes a protein(s) of 42-45 kDa with the same N-terminal amino acid sequence as the membrane-bound portion of mesothelin and megakaryocyte potentiating factor (MPF). Binding assays with fusion proteins comprising either the N-terminal part of mesothelin/MPF (D1Ig), reported to be easily cleaved off, or a noncleavable, membrane-associated part (D2Ig) showed that OV569 only binds to D2hIg. A new member of the mesothelin/MPF family was discovered, which has an 82-bp insert in the membrane-associated part, leading to a frameshift of 212 bp, and whose predicted molecular structure indicates that it is soluble. To test patient sera for soluble tumor antigen, antigen was isolated from cell-free tumor culture supernatants via immunoadsorption with OV569 and used to generate murine mAbs to an epitope different from the one to which OV569 binds, after which mAbs to two different epitopes were used to develop a "sandwich ELISA." Using this assay, the level of circulating antigen was elevated significantly in 23 of 30 sera from patients with ovarian carcinoma, as compared with 0 of 68 sera from healthy controls, 0 of 3 sera from patients with nonneoplastic diseases, and 25 of 75 sera from patients with other tumors. Soluble molecules of the mesothelin/MPF family may provide useful new marker(s) for diagnosis of ovarian carcinoma and/or monitoring its response to therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Jacobs I, Bast R C. Hum Repro. 1989;4:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Mazurek A, Niklinski J, Laudanski T, Pluygers E. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1998;7:23–35. - PubMed
-
- Berek J S, Bast R C., Jr Cancer. 1995;76:2092–2096. - PubMed
-
- Guadagni F, Roselli M, Cosimelli M, Ferroni P, Spila A, Cavaliere F, Casaldi V, Wappner G, Abbolito M R, Greiner J W, et al. Cancer Invest. 1995;13:227–238. - PubMed
-
- Pannek J, Partin A W. Semin Urol Oncol. 1998;16:100–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

