Penetration of topical, oral, and combined administered ofloxacin into the subretinal fluid
- PMID: 10502583
- PMCID: PMC1722819
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.83.10.1183
Penetration of topical, oral, and combined administered ofloxacin into the subretinal fluid
Abstract
Aims: To assess the subretinal fluid (SRF) levels of ofloxacin following topical, oral or combined administration.
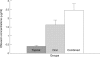
Methods: 31 patients undergoing conventional retinal reattachment surgery were randomly assigned to three groups. Nine patients received topical ofloxacin, 11 patients received oral ofloxacin, and the other 11 patients received combined administration. Collected SRF samples were analysed for drug level by using high performance liquid chromatography.
Results: SRF drug levels after oral and combined administration were significantly higher than that after topical administration (p=0.0002 and p=0.0002, respectively) while there was no significant difference between oral and combined administration (p=0.0844).
Conclusions: Ocular bioavailability of ofloxacin in SRF after oral and combined administration is equivalent. The addition of oral ofloxacin to topical therapy increased drug SRF penetration sixfold.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subretinal fluid levels of topical, oral, and combined administered ciprofloxacin in humans.Br J Ophthalmol. 2000 Sep;84(9):1061-3. doi: 10.1136/bjo.84.9.1061. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000. PMID: 10966968 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Penetration of ofloxacin in human aqueous and vitreous humors following oral and topical administration.Retina. 1998;18(6):521-5. doi: 10.1097/00006982-199806000-00005. Retina. 1998. PMID: 9869460
-
Retinal safety of oral and topical ofloxacin in rabbits.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Aug;13(4):369-79. doi: 10.1089/jop.1997.13.369. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 1997. PMID: 9261772
-
[Pharmacokinetic properties of ofloxacin (review of the literature].Antibiot Khimioter. 1996;41(9):24-32. Antibiot Khimioter. 1996. PMID: 9005781 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
-
Ofloxacin and the gastrointestinal tract: a potential role in the treatment of bacterial enteritis.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Nov;26 Suppl D:45-53. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.suppl_d.45. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990. PMID: 2286590 Review.
Cited by
-
Subretinal fluid levels of topical, oral, and combined administered ciprofloxacin in humans.Br J Ophthalmol. 2000 Sep;84(9):1061-3. doi: 10.1136/bjo.84.9.1061. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000. PMID: 10966968 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Administration of oral fluoroquinolone and the risk of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: A nationwide population-based study in Korea.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 12;13(4):e0195563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195563. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29649310 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and prevention of ocular phototoxicity of ciprofloxacin and other fluoroquinolone antibiotics.Photochem Photobiol. 2010 Jul-Aug;86(4):798-805. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2010.00755.x. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Photochem Photobiol. 2010. PMID: 20528972 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous