Inhibition of dibenzo[a,l]pyrene-induced multi-organ carcinogenesis by dietary chlorophyllin in rainbow trout
- PMID: 10506105
- PMCID: PMC2386994
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/20.10.1919
Inhibition of dibenzo[a,l]pyrene-induced multi-organ carcinogenesis by dietary chlorophyllin in rainbow trout
Abstract
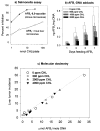
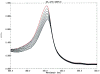
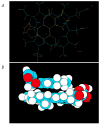
Cancer chemoprevention by dietary chlorophyllin (CHL) was investigated in a rainbow trout multi-organ tumor model. In study 1, duplicate groups of 130 juvenile trout were treated for 2 weeks with control diet, 500 p.p.m. dibenzo[a,l]pyrene (DB[a,l]P) or 500 p.p.m. DB[a,l]P + 2052 p.p.m. CHL, then returned to control diet. DB[a,l]P alone proved somewhat toxic but induced high tumor incidences in liver (61%), stomach (91%) and swimbladder (53%) 11 months after initiation. CHL co-feeding abrogated DB[a,l]P acute toxicity and reduced tumor incidences to 18% in liver, 34% in stomach and 3% in swimbladder (P </= 0.01). A second tumor and DNA adduct study using a non-toxic initiation protocol (200 p.p.m. DB[a,l]P +/- 4000 p.p.m. CHL for 4 weeks) confirmed these results. Potential CHL inhibitory mechanisms were investigated. Dietary CHL inhibited hepatic DB[a, l]P-DNA adducts in the two tumor studies by 89 and 76%, respectively. CHL was shown to complex strongly with DB[a,l]P (K(d1,2) = 1.59 +/- 0.01 microM, stoichiometry 2CHL:DB[a,l]P) and strongly inhibited DB[a,l]P mutagenesis in the Salmonella assay. Significant inhibition occurred at CHL concentrations substantially less than stoichiometric with DB[a,l]P and thus not reflecting simple DB[a,l]P sequestration via complexation. These initial findings suggest that CHL chemoprevention reflects complexation that might limit DB[a,l]P uptake in vivo, antimutagenic mechanisms such as catalytic degradation of the proximate electrophile in target cells, or both. These results demonstrate that dietary CHL is a reproducibly effective chemopreventive agent for DB[a,l]P multi-organ tumorigenesis in trout and suggest that reduced DB[a,l]P-DNA adducts may be predictive biomarkers of CHL reduction of DB[a,l]P-initiated hepatic tumors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The importance of carcinogen dose in chemoprevention studies: quantitative interrelationships between, dibenzo[a,l]pyrene dose, chlorophyllin dose, target organ DNA adduct biomarkers and final tumor outcome.Carcinogenesis. 2007 Mar;28(3):611-24. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl174. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Carcinogenesis. 2007. PMID: 16973675
-
Low-dose dietary chlorophyll inhibits multi-organ carcinogenesis in the rainbow trout.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Mar;46(3):1014-24. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.10.034. Epub 2007 Nov 4. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18069110 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoprotection by natural chlorophylls in vivo: inhibition of dibenzo[a,l]pyrene-DNA adducts in rainbow trout liver.Carcinogenesis. 1998 Jul;19(7):1323-6. doi: 10.1093/carcin/19.7.1323. Carcinogenesis. 1998. PMID: 9683196
-
Chemopreventive properties of chlorophylls towards aflatoxin B1: a review of the antimutagenicity and anticarcinogenicity data in rainbow trout.Mutat Res. 1998 Mar 20;399(2):245-53. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(97)00259-5. Mutat Res. 1998. PMID: 9672663 Review.
-
The rainbow trout liver cancer model: response to environmental chemicals and studies on promotion and chemoprevention.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;155(1):121-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2011.05.013. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21704190 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neoplasia and neoplasm-associated lesions in laboratory colonies of zebrafish emphasizing key influences of diet and aquaculture system design.ILAR J. 2012;53(2):114-25. doi: 10.1093/ilar.53.2.114. ILAR J. 2012. PMID: 23382343 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Models Fit to ED001 Data on >40,000 Trout Exposed to Dibenzo[A,L]pyrene Indicate Mutations Do Not Drive Increased Tumor Risk.Dose Response. 2014 Jan 10;12(3):386-403. doi: 10.2203/dose-response.13-019.Bogen. eCollection 2014 Jul. Dose Response. 2014. PMID: 25249832 Free PMC article.
-
Development of rainbow trout hepatoma cell lines: effect of pro-IGF-I Ea4-peptide on morphological changes and anchorage-independent growth.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2004 Mar-Apr;40(3-4):118-28. doi: 10.1290/1543-706x(2004)040<0118:dorthc>2.0.co;2. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2004. PMID: 15311963
-
The "interceptor" properties of chlorophyllin measured within the three-component system: intercalator-DNA-chlorophyllin.Biophys Chem. 2006 Aug 20;123(1):11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2006.03.018. Epub 2006 Apr 6. Biophys Chem. 2006. PMID: 16650923 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of acridine mutagen ICR-191--DNA interactions and DNA damage by the mutagen interceptor chlorophyllin.Biophys Chem. 2008 Jun;135(1-3):69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2008.03.004. Epub 2008 Mar 30. Biophys Chem. 2008. PMID: 18423964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Waters MD, Stack HF, Jackson MA, Brockman HE, De Flora S. Activity profiles of antimutagens: in vitro and in vivo data. Mutat Res. 1996;350:109–129. - PubMed
-
- Breinholt V, Hendricks J, Pereira C, Arbogast D, Bailey G. Dietary chlorophyllin is a potent inhibitor of aflatoxin B1 hepatocarcinogenesis in rainbow trout. Cancer Res. 1995;55:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Whong WZ, Stewart J, Brockman HE, Ong T. Comparative anti-mutagenicity of chlorophyllin and five other agents against aflatoxin B1-induced reversion in Salmonella typhimurium strain TA98. Teratog Carcinog Mutag. 1988;8:215–224. - PubMed
-
- Dashwood RH, Breinholt V, Bailey GS. Chemopreventive properties of chlorophyllin: inhibition of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1)-DNA binding in vivo and anti-mutagenic activity against AFB1 and two heterocyclic amines in the Salmonella mutagenicity assay. Carcinogenesis. 1991;12:939–942. - PubMed
-
- Dashwood RH, Arbogast D, Fong AT, Hendricks JD, Bailey GS. Mechanisms of anti-carcinogenesis by indole-3-carbinol: Detailed in vivo DNA binding dose-response studies after dietary administration with AFB1. Carcinogenesis. 1988;9:427–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

