Population structure and phylogenetic characterization of marine benthic Archaea in deep-sea sediments
- PMID: 10508063
- PMCID: PMC91581
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.10.4375-4384.1999
Population structure and phylogenetic characterization of marine benthic Archaea in deep-sea sediments
Abstract
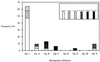
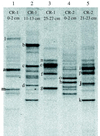
During the past few years Archaea have been recognized as a widespread and significant component of marine picoplankton assemblages and, more recently, the presence of novel archaeal phylogenetic lineages has been reported in coastal marine benthic environments. We investigated the relative abundance, vertical distribution, phylogenetic composition, and spatial variability of Archaea in deep-sea sediments collected from several stations in the Atlantic Ocean. Quantitative oligonucleotide hybridization experiments indicated that the relative abundance of archaeal 16S rRNA in deep-sea sediments (1500 m deep) ranged from about 2.5 to 8% of the total prokaryotic rRNA. Clone libraries of PCR-amplified archaeal rRNA genes (rDNA) were constructed from 10 depth intervals obtained from sediment cores collected at depths of 1,500, 2,600, and 4,500 m. Phylogenetic analysis of rDNA sequences revealed the presence of a complex archaeal population structure, whose members could be grouped into discrete phylogenetic lineages within the two kingdoms, Crenarchaeota and Euryarchaeota. Comparative denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profile analysis of archaeal 16S rDNA V3 fragments revealed a significant depth-related variability in the composition of the archaeal population.
Figures




References
-
- Aller R C, Hall P O J, Rude P D, Aller J Y. Biogeochemical heterogeneity and suboxic diagenesis in hemipelagic sediments of the Panama Basin. Deep-Sea Res. 1998;45:133–165.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

