Diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in oxic and anoxic regions of a microbial mat characterized by comparative analysis of dissimilatory sulfite reductase genes
- PMID: 10508104
- PMCID: PMC91622
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.10.4666-4671.1999
Diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in oxic and anoxic regions of a microbial mat characterized by comparative analysis of dissimilatory sulfite reductase genes
Abstract
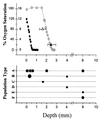
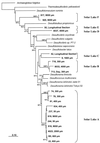
Sequence analysis of genes encoding dissimilatory sulfite reductase (DSR) was used to identify sulfate-reducing bacteria in a hypersaline microbial mat and to evaluate their distribution in relation to levels of oxygen. The most highly diverse DSR sequences, most related to those of the Desulfonema-like organisms within the delta-proteobacteria, were recovered from oxic regions of the mat. This observation extends those of previous studies by us and others associating Desulfonema-like organisms with oxic habitats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bacterial enzymes for dissimilatory sulfate reduction in a marine microbial mat (Black Sea) mediating anaerobic oxidation of methane.Environ Microbiol. 2011 May;13(5):1370-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02443.x. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21392199
-
Congruent phylogenies of most common small-subunit rRNA and dissimilatory sulfite reductase gene sequences retrieved from estuarine sediments.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Jul;67(7):3314-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.7.3314-3318.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11425760 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeny of dissimilatory sulfite reductases supports an early origin of sulfate respiration.J Bacteriol. 1998 Jun;180(11):2975-82. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.11.2975-2982.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9603890 Free PMC article.
-
Origins and diversification of sulfate-respiring microorganisms.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002 Aug;81(1-4):189-95. doi: 10.1023/a:1020506415921. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2002. PMID: 12448717 Review.
-
Enzymology and molecular biology of prokaryotic sulfite oxidation.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001 Sep 11;203(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10813.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11557133 Review.
Cited by
-
High rates of sulfate reduction in a low-sulfate hot spring microbial mat are driven by a low level of diversity of sulfate-respiring microorganisms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Aug;73(16):5218-26. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00357-07. Epub 2007 Jun 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17575000 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected population distribution in a microbial mat community: sulfate-reducing bacteria localized to the highly oxic chemocline in contrast to a eukaryotic preference for anoxia.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Oct;65(10):4659-65. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.10.4659-4665.1999. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10508103 Free PMC article.
-
Nested PCR and new primers for analysis of sulfate-reducing bacteria in low-cell-biomass environments.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 May;76(9):2856-65. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02023-09. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20228118 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic of sulphate-reducing microorganisms in petroleum-contaminated marine sediments inhabited by the polychaete Hediste diversicolor.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Oct;22(20):15273-84. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3624-y. Epub 2014 Sep 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25256587
-
Sulfate reduction and possible aerobic metabolism of the sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio oxyclinae in a chemostat coculture with Marinobacter sp. Strain MB under exposure to increasing oxygen concentrations.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Nov;66(11):5013-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.11.5013-5018.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11055957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdollahi H, Wimpenny J W T. Effects of oxygen on the growth of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Gen Microbiol. 1990;136:1025–1030.
-
- Canfield D E, Des Marais D J. Aerobic sulfate reduction in microbial mats. Science. 1991;251:1471–1473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

