Viability and DNA maintenance in nonculturable spiral Campylobacter jejuni cells after long-term exposure to low temperatures
- PMID: 10508106
- PMCID: PMC91624
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.10.4677-4681.1999
Viability and DNA maintenance in nonculturable spiral Campylobacter jejuni cells after long-term exposure to low temperatures
Abstract
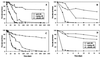
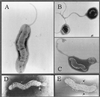
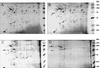
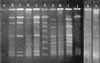
Survival of Campylobacter jejuni at 4 and 20 degrees C was investigated by using cellular integrity, respiratory activity, two-dimensional (2D) protein profile, and intact DNA content as indicators of potential viability of nonculturable cells. Intact DNA content after 116 days, along with cellular integrity and respiring cells, was detected for up to 7 months at 4 degrees C by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Most changes in 2D protein profiles involved up- or down-regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Temperature-dependent genome degradation in the coccoid form of Campylobacter jejuni.Curr Microbiol. 2005 Feb;50(2):110-3. doi: 10.1007/s00284-004-4400-x. Epub 2005 Feb 8. Curr Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15742237
-
Molecular strain typing of Campylobacter jejuni by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis in a single day.Can J Microbiol. 2001 Jul;47(7):667-9. Can J Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11547887
-
Pulsed-field gel electrophoretic analysis of Campylobacter jejuni DNA for use in epidemiological studies.J Infect. 1993 Jul;27(1):39-42. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(93)93628-h. J Infect. 1993. PMID: 8370943
-
Morphological and physiological responses of Campylobacter jejuni to stress.J Food Prot. 2006 Nov;69(11):2747-53. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-69.11.2747. J Food Prot. 2006. PMID: 17133821
-
Inhibition of DNAse activity in PFGE analysis of DNA from Campylobacter jejuni.Lett Appl Microbiol. 1994 Nov;19(5):357-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1994.tb00474.x. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 7765449
Cited by
-
Survival of clinical and poultry-derived isolates of Campylobacter jejuni at a low temperature (4 degrees C).Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Sep;67(9):4186-91. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.9.4186-4191.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11526022 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Effect of Management Practices on Campylobacter Prevalence in Poultry Farms.Front Microbiol. 2018 Aug 24;9:2002. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02002. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30197638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid and sensitive isolation of Campylobacter jejuni using immunomagnetic separation from patient specimens exposed to oxygen.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Apr;13(4):e0190724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01907-24. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39964178 Free PMC article.
-
Campylobacter jejuni transcriptome changes during loss of culturability in water.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 30;12(11):e0188936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188936. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29190673 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of mono- and mixed-culture Campylobacter jejuni biofilms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Feb;78(4):1033-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.07364-11. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22179238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arana I, Pocino M, Muela A, Fernández-Astorga A, Barcina I. Detection and enumeration of viable but non-culturable transconjugants of Escherichia coli during the survival of recipient cells in river water. J Appl Microbiol. 1997;83:340–346. - PubMed
-
- Boucher S N, Slater E R, Chamberlain A H L, Adams M R. Production and viability of coccoid forms of Campylobacter jejuni. J Appl Bacteriol. 1994;77:303–307. - PubMed
-
- Buswell C M, Herlihy Y M, Lawrence L M, McGuiggan J T M, Marsh P D, Keevil C W, Leach S A. Extended survival and persistence of Campylobacter spp. in water and aquatic biofilms and their detection by immunofluorescent-antibody and rRNA staining. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998;64:733–741. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cappelier J M, Lázaro B, Rossero A, Fernández-Astorga A, Federighi M. Double staining (CTC-DAPI) for detection and enumeration of viable but non-culturable Campylobacter jejuni cells. Vet Res. 1997;28:547–555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

