Detection and differentiation of Listeria spp. by a single reaction based on multiplex PCR
- PMID: 10508109
- PMCID: PMC91627
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.10.4688-4692.1999
Detection and differentiation of Listeria spp. by a single reaction based on multiplex PCR
Abstract
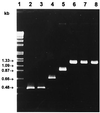
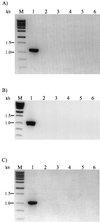
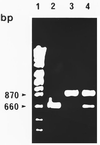
The iap gene encodes the protein p60, which is common to all Listeria species. A previous comparison of the DNA sequences indicated conserved and species-specific gene portions. Based on these comparisons, a combination consisting of only five different primers that allows the specific detection and differentiation of Listeria species with a single multiplex PCR and subsequent gel analysis was selected. One primer was derived from the conserved 3' end and is specific for all Listeria species; the other four primers are specific for Listeria monocytogenes, L. innocua, L. grayi, or the three grouped species L. ivanovii, L. seeligeri, and L. welshimeri, respectively. The PCR method, which also enables the simultaneous detection of L. monocytogenes and L. innocua, was evaluated against conventional biotyping with 200 food hygiene-relevant Listeria strains. The results indicated the superiority of this technique. Thus, this novel type of multiplex PCR may be useful for rapid Listeria species confirmation and for identification of Listeria species for strains isolated from different sources.
Figures



References
-
- Allerberger F, Dierich M, Petranyi G, Lalic M, Bubert A. Nonhemolytic strains of Listeria monocytogenes detected in milk products using VIDAS immunoassay kit. Zentbl Hyg. 1997;200:189–195. - PubMed
-
- Bubert A, Kestler H, Götz M, Böckmann R, Goebel W. The Listeria monocytogenes iap gene as an indicator gene for the study of PrfA-dependent regulation. Mol Gen Genet. 1997;256:54–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

